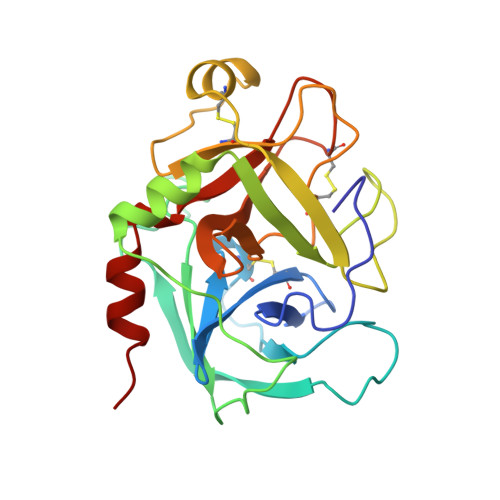
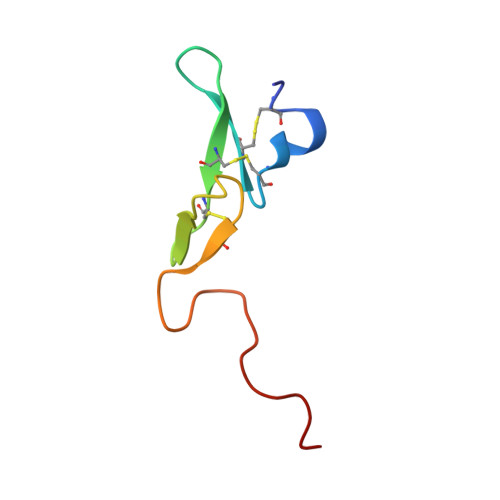
Coagulation factor IXa: the relaxed conformation of Tyr99 blocks substrate binding.
Hopfner, K.P., Lang, A., Karcher, A., Sichler, K., Kopetzki, E., Brandstetter, H., Huber, R., Bode, W., Engh, R.A.(1999) Structure 7: 989-996
- PubMed: 10467148
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80125-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RFN - PubMed Abstract:
Among the S1 family of serine proteinases, the blood coagulation factor IXa (fIXa) is uniquely inefficient against synthetic peptide substrates. Mutagenesis studies show that a loop of residues at the S2-S4 substrate-binding cleft (the 99-loop) contributes to the low efficiency. The crystal structure of porcine fIXa in complex with the inhibitor D-Phe-Pro-Arg-chloromethylketone (PPACK) was unable to directly clarify the role of the 99-loop, as the doubly covalent inhibitor induced an active conformation of fIXa. The crystal structure of a recombinant two-domain construct of human fIXa in complex with p-aminobenzamidine shows that the Tyr99 sidechain adopts an atypical conformation in the absence of substrate interactions. In this conformation, the hydroxyl group occupies the volume corresponding to the mainchain of a canonically bound substrate P2 residue. To accommodate substrate binding, Tyr99 must adopt a higher energy conformation that creates the S2 pocket and restricts the S4 pocket, as in fIXa-PPACK. The energy cost may contribute significantly to the poor K(M) values of fIXa for chromogenic substrates. In homologs, such as factor Xa and tissue plasminogen activator, the different conformation of the 99-loop leaves Tyr99 in low-energy conformations in both bound and unbound states. Molecular recognition of substrates by fIXa seems to be determined by the action of the 99-loop on Tyr99. This is in contrast to other coagulation enzymes where, in general, the chemical nature of residue 99 determines molecular recognition in S2 and S3-S4. This dominant role on substrate interaction suggests that the 99-loop may be rearranged in the physiological fX activation complex of fIXa, fVIIIa, and fX.
Organizational Affiliation:
Abteilung Strukturforschung, Max-Planck-Institut f¨¹r Biochemie, Martinsried, Germany.