The HIV-1 Capsid Protein C-Terminal Domain in Complex with a Virus Assembly Inhibitor
Ternois, F., Sticht, J., Duquerroy, S., Krausslich, H.-G., Rey, F.A.(2005) Nat Struct Mol Biol 12: 678
- PubMed: 16041386
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb967
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BUO - PubMed Abstract:
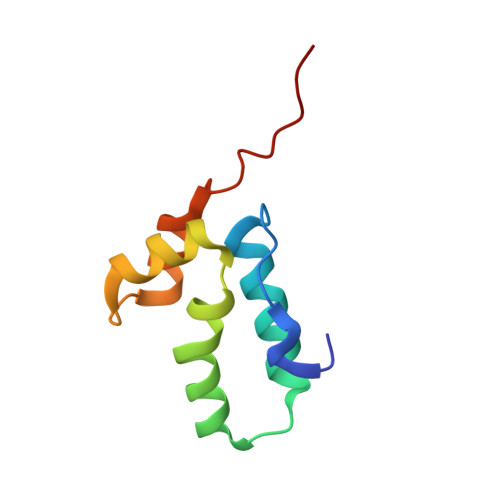
Immature HIV particles bud from infected cells after assembly at the cytoplasmic side of cellular membranes. This assembly is driven by interactions between Gag polyproteins. Mature particles, each containing a characteristic conical core, are later generated by proteolytic maturation of Gag in the virion. The C-terminal domain of the HIV-1 capsid protein (C-CA) has been shown to contain oligomerization determinants essential for particle assembly. Here we report the 1.7-A-resolution crystal structure of C-CA in complex with a peptide capable of inhibiting immature- and mature-like particle assembly in vitro. The peptide inserts as an amphipathic alpha-helix into a conserved hydrophobic groove of C-CA, resulting in formation of a compact five-helix bundle with altered dimeric interactions. This structure thus reveals the details of an allosteric site in the HIV capsid protein that can be targeted for antiviral therapy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire de Virologie Mol¨¦culaire & Structurale, UMR 2472/1157 CNRS-INRA and IFR 115, Avenue de la Terrasse, 91198 Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France.