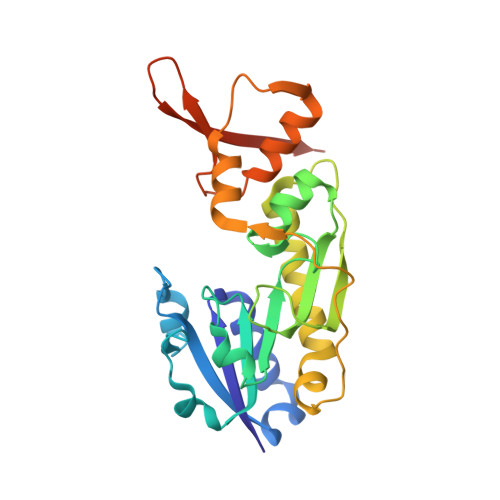
Molecular structure of an N-formyltransferase from Providencia alcalifaciens O30.
Genthe, N.A., Thoden, J.B., Benning, M.M., Holden, H.M.(2015) Protein Sci 24: 976-986
- PubMed: 25752909
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2675
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4YFV, 4YFY - PubMed Abstract:
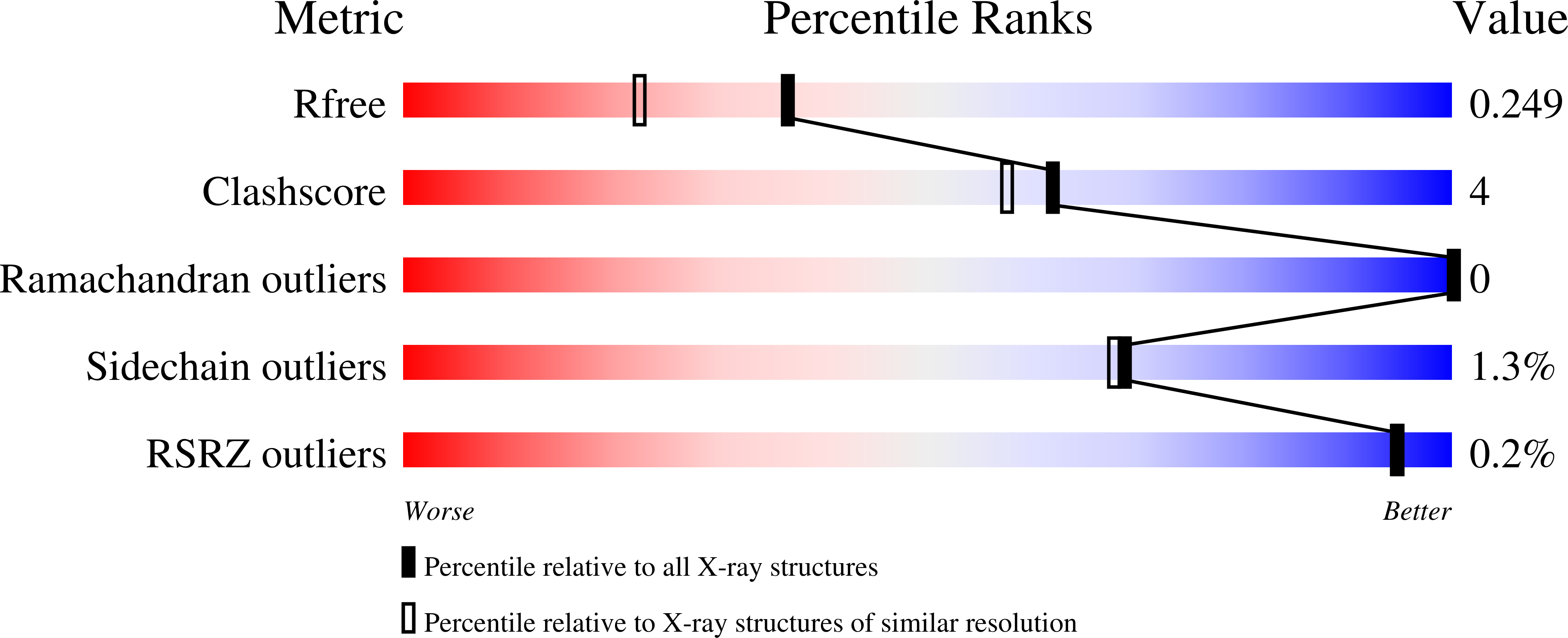
The existence of N-formylated sugars in the O-antigens of Gram-negative bacteria has been known since the middle 1980s, but only recently have the biosynthetic pathways for their production been reported. In these pathways, glucose-1-phosphate is first activated by attachment to a dTMP moiety. This step is followed by a dehydration reaction and an amination. The last step in these pathways is catalyzed by N-formyltransferases that utilize N(10) -formyltetrahydrofolate as the carbon source. Here we describe the three-dimensional structure of one of these N-formyltransferases, namely VioF from Providencia alcalifaciens O30. Specifically, this enzyme catalyzes the conversion of dTDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxyglucose (dTDP-Qui4N) to dTDP-4,6-dideoxy-4-formamido-d-glucose (dTDP-Qui4NFo). For this analysis, the structure of VioF was solved to 1.9 ? resolution in both its apoform and in complex with tetrahydrofolate and dTDP-Qui4N. The crystals used in the investigation belonged to the space group R32 and demonstrated reticular merohedral twinning. The overall catalytic core of the VioF subunit is characterized by a six stranded mixed ¦Â-sheet flanked on one side by three ¦Á-helices and on the other side by mostly random coil. This N-terminal domain is followed by an ¦Á-helix and a ¦Â-hairpin that form the subunit:subunit interface. The active site of the enzyme is shallow and solvent-exposed. Notably, the pyranosyl moiety of dTDP-Qui4N is positioned into the active site by only one hydrogen bond provided by Lys 77. Comparison of the VioF model to that of a previously determined N-formyltransferase suggests that substrate specificity is determined by interactions between the protein and the pyrophosphoryl group of the dTDP-sugar substrate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, 53706.