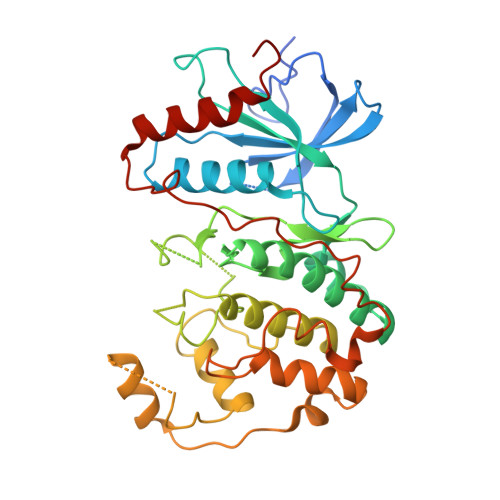
Identification of allosteric ERK2 inhibitors through in silico biased screening and competitive binding assay
Kinoshita, T., Sugiyama, H., Mori, Y., Takahashi, N., Tomonaga, A.(2016) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 955-958
- PubMed: 26733474
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.12.056
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5AX3 - PubMed Abstract:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) is a drug target for type 2 diabetes mellitus. A peptide-type ERK2 inhibitor (PEP) was discovered in the previous study through the knowledge-based method and showed physiological effects on the db/db mice model of type 2 diabetes. Here, the crystal structure showed that PEP bound to the allosteric site without the interruption of the ATP competitive inhibitor binding to ERK2. An in silico biased-screening using the focused library rendered three compounds with inhibitory activity of IC50 <100 ¦̀M. Among them, two compounds revealed the concentration-dependent competition with PEP and could be lead compounds for antidiabetic medicine.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Science, Osaka Prefecture University, 1-1 Gakuen-cho, Naka-ku, Sakai, Osaka 599-8531, Japan. Electronic address: kinotk@b.s.osakafu-u.ac.jp.