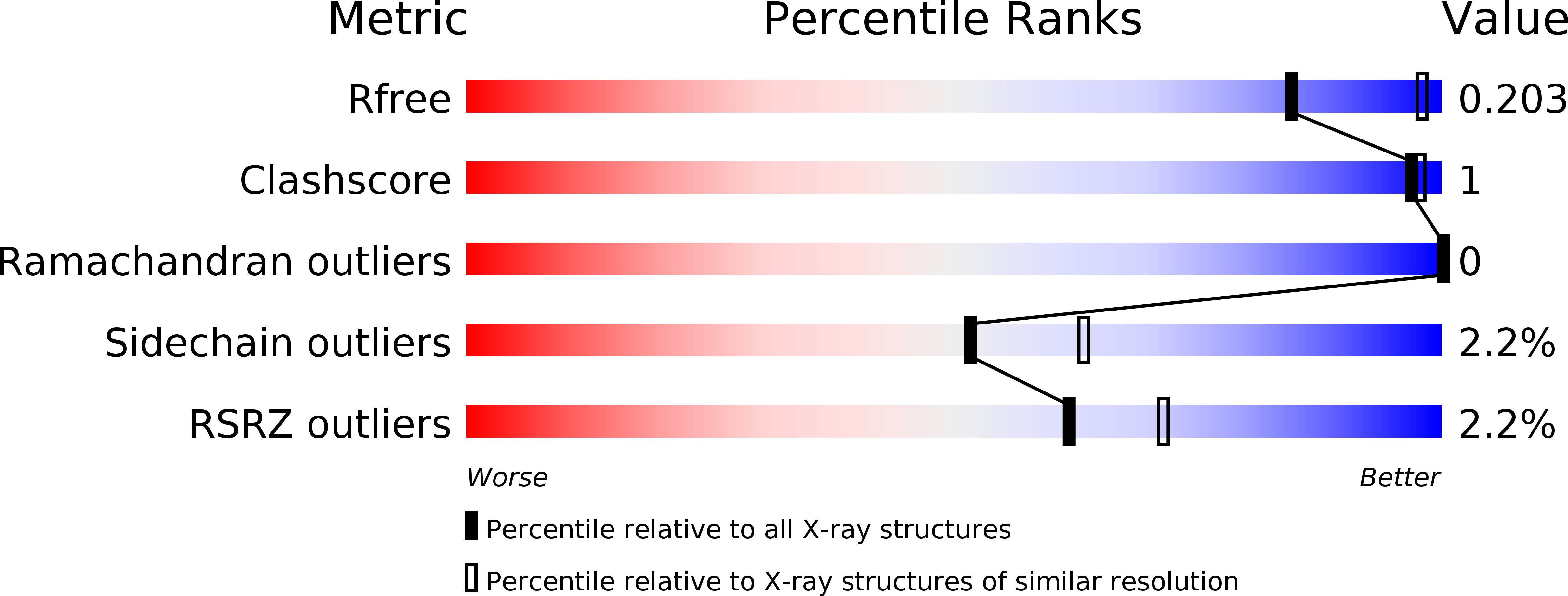
Potent, selective and orally bioavailable leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) inhibitors.
Greshock, T.J., Sanders, J.M., Drolet, R.E., Rajapakse, H.A., Chang, R.K., Kim, B., Rada, V.L., Tiscia, H.E., Su, H., Lai, M.T., Sur, S.M., Sanchez, R.I., Bilodeau, M.T., Renger, J.J., Kern, J.T., McCauley, J.A.(2016) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 2631-2635
- PubMed: 27106707
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5I8A - PubMed Abstract:
Familial Parkinson's disease cases have recently been associated with the leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene. It has been hypothesized that inhibition of the LRRK2 protein may have the potential to alter disease pathogenesis. A dihydrobenzothiophene series of potent, selective, orally bioavailable LRRK2 inhibitors were identified from a high-throughput screen of the internal Merck sample collection. Initial SAR studies around the core established the series as a tractable small molecule lead series of LRRK2 inhibitors for potential treatment of Parkinson's disease. It was also found that incorporation of a lactam into the core drastically improved the CNS and DMPK properties of these small molecules.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Merck Research Laboratories, West Point, PA 19486, United States. Electronic address: thomas_greshock@merck.com.