Complex Crystal Structure Determination and in vitro Anti-non-small Cell Lung Cancer Activity of Hsp90 N Inhibitor SNX-2112.
Zhao, D., Xu, Y.M., Cao, L.Q., Yu, F., Zhou, H., Qin, W., Li, H.J., He, C.X., Xing, L., Zhou, X., Li, P.Q., Jin, X., He, Y., He, J.H., Cao, H.L.(2021) Front Cell Dev Biol 9: 650106-650106
- PubMed: 33855025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.650106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LTK - PubMed Abstract:
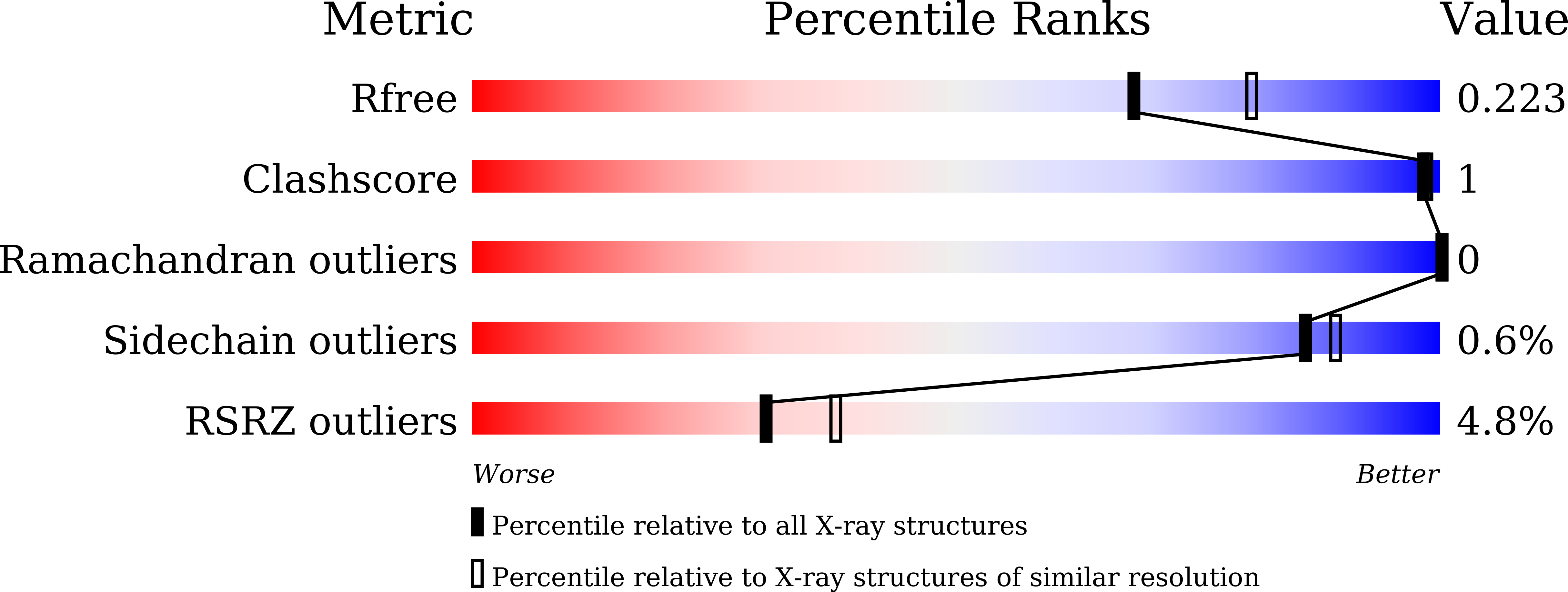
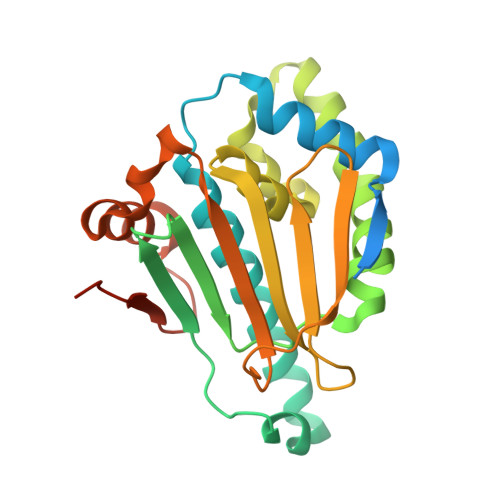
SNX-2112, as a promising anticancer lead compound targeting heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90), absence of complex crystal structure of Hsp90 N -SNX-2112 hindered further structural optimization and understanding on molecular interaction mechanism. Herein, a high-resolution complex crystal structure of Hsp90 N -SNX-2112 was successfully determined by X-ray diffraction, resolution limit, 2.14 ?, PDB ID 6LTK, and their molecular interaction was analyzed in detail, which suggested that SNX-2112 was well accommodated in the ATP-binding pocket to disable molecular chaperone activity of Hsp90, therefore exhibiting favorable inhibiting activity on three non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines (IC 50 , 0.50 ¡À 0.01 ¦ÌM for A549, 1.14 ¡À 1.11 ¦ÌM for H1299, 2.36 ¡À 0.82 ¦ÌM for H1975) by inhibited proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest, and aggravated cell apoptosis. SNX-2112 exhibited high affinity and beneficial thermodynamic changes during the binding process with its target Hsp90 N confirmed by thermal shift assay (TSA, ¦¤Tm, and -9.51 ¡À 1.00¡ãC) and isothermal titration calorimetry ( K d , 14.10 ¡À 1.60 nM). Based on the complex crystal structure and molecular interaction analysis, 32 novel SNX-2112 derivatives were designed, and 25 new ones displayed increased binding force with the target Hsp90 N verified by molecular docking evaluation. The results would provide new references and guides for anti-NSCLC new drug development based on the lead compound SNX-2112.
Organizational Affiliation:
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Ischemic Cardiovascular Disease, Institute of Basic & Translational Medicine, Xi'an Medical University, Xi'an, China.