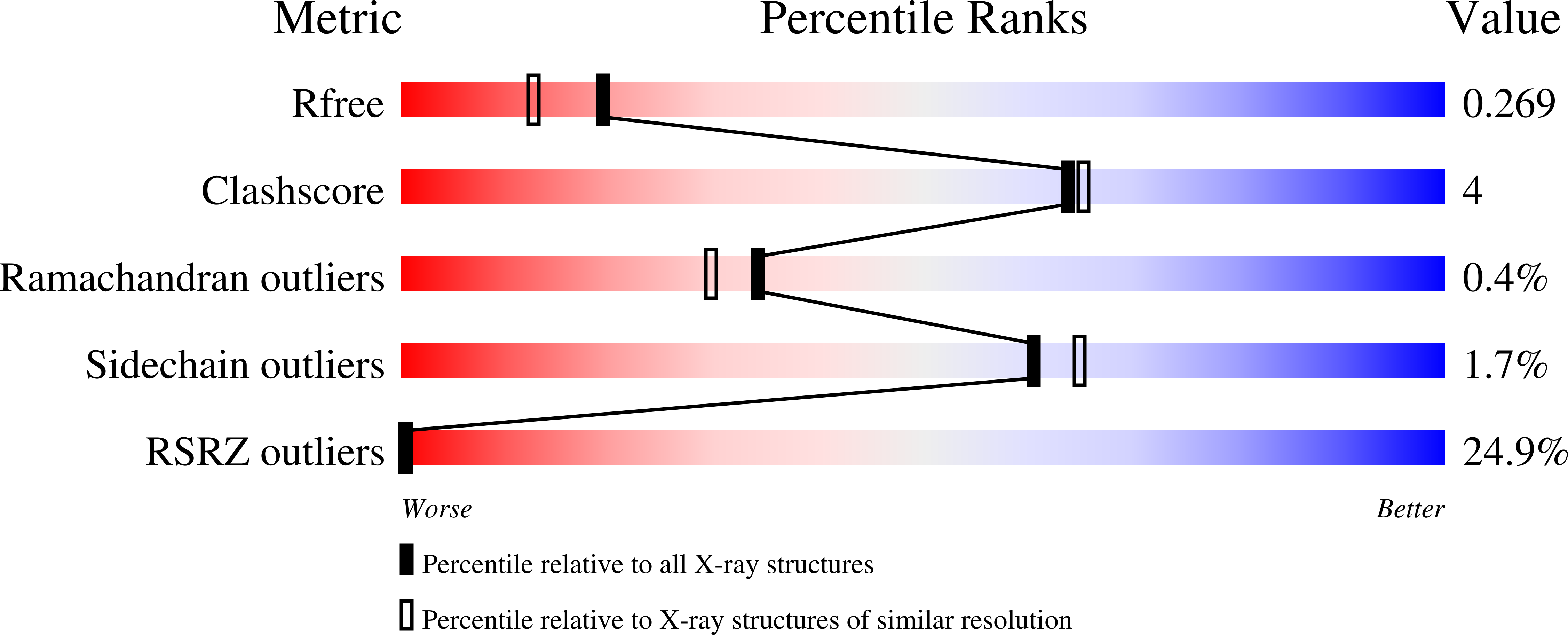
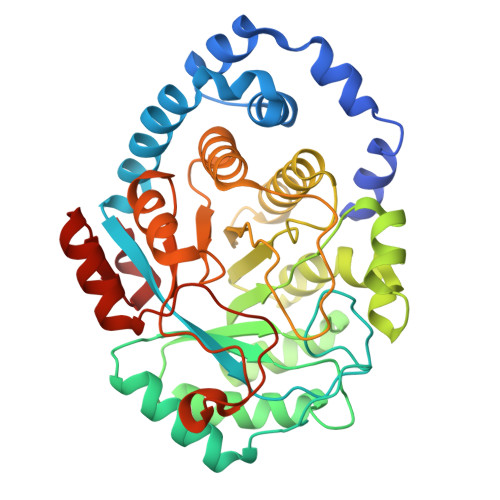
L-tyrosine-bound ThiH structure reveals C-C bond break differences within radical SAM aromatic amino acid lyases.
Amara, P., Saragaglia, C., Mouesca, J.M., Martin, L., Nicolet, Y.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 2284-2284
- PubMed: 35477710
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29980-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7PD1, 7PD2 - PubMed Abstract:
2-iminoacetate synthase ThiH is a radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) L-tyrosine lyase and catalyzes the L-tyrosine C¦Á-C¦Â bond break to produce dehydroglycine and p-cresol while the radical SAM L-tryptophan lyase NosL cleaves the L-tryptophan C¦Á-C bond to produce 3-methylindole-2-carboxylic acid. It has been difficult to understand the features that condition one C-C bond break over the other one because the two enzymes display significant primary structure similarities and presumably similar substrate-binding modes. Here, we report the crystal structure of L-tyrosine bound ThiH from Thermosinus carboxydivorans revealing an unusual protonation state of L-tyrosine upon binding. Structural comparison of ThiH with NosL and computational studies of the respective reactions they catalyze show that substrate activation is eased by tunneling effect and that subtle structural changes between the two enzymes affect, in particular, the hydrogen-atom abstraction by the 5?-deoxyadenosyl radical species, driving the difference in reaction specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Univ. Grenoble Alpes, CEA, CNRS, IBS, Metalloproteins Unit, F-38000, Grenoble, France.