Fragment-Based Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Aminoisoindole-Derived Furin Inhibitors.
Lange, R.W., Bloch, K., Heindl, M.R., Wollenhaupt, J., Weiss, M.S., Brandstetter, H., Klebe, G., Falcone, F.H., Bottcher-Friebertshauser, E., Dahms, S.O., Steinmetzer, T.(2024) ChemMedChem 19: e202400057-e202400057
- PubMed: 38385828
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202400057
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
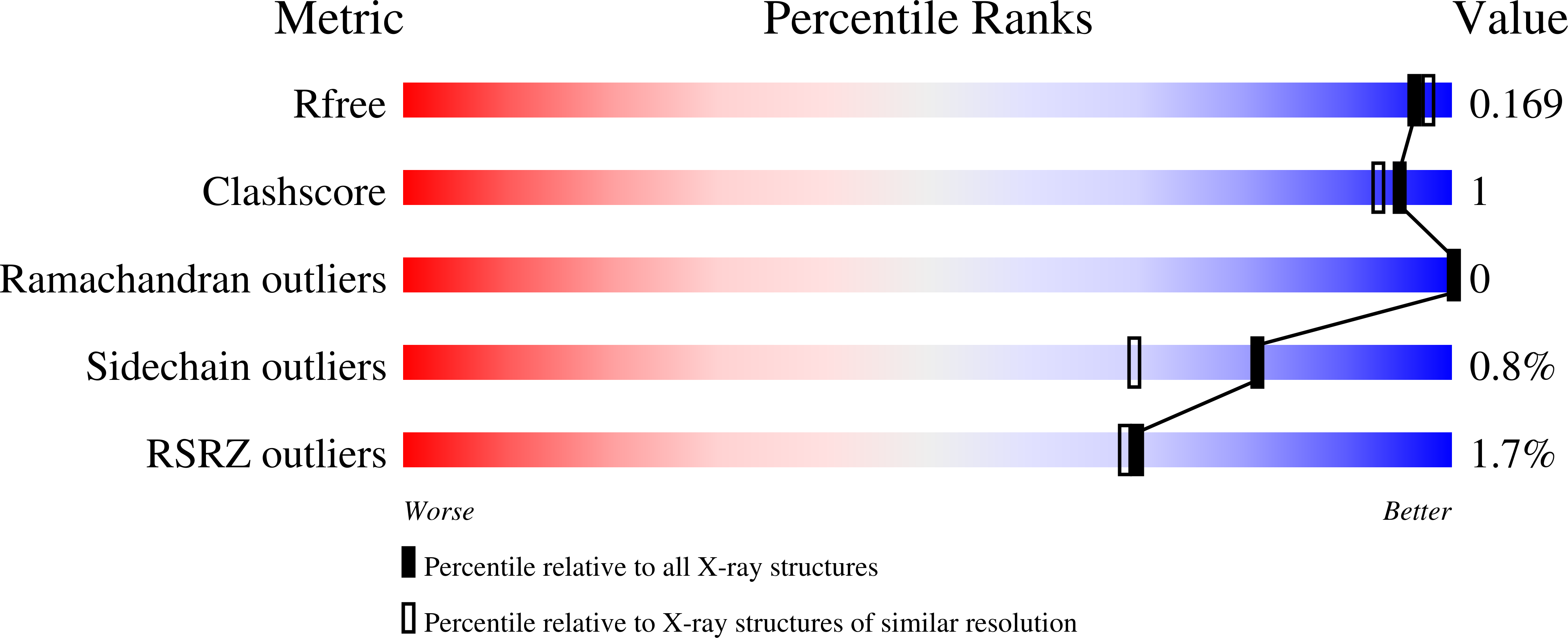
8B4V, 8B4W, 8B4X, 8OYH - PubMed Abstract:
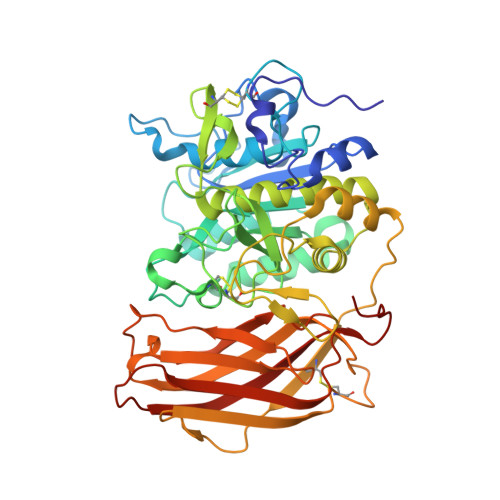
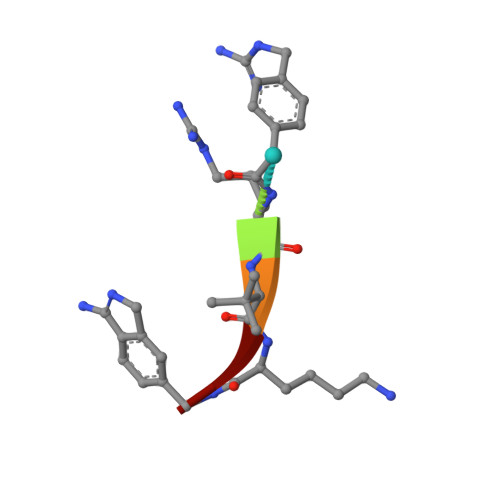
A 1H-isoindol-3-amine was identified as suitable P1 group for the proprotein convertase furin using a crystallographic screening with a set of 20 fragments known to occupy the S1 pocket of trypsin-like serine proteases. Its binding mode is very similar to that observed for the P1 group of benzamidine-derived peptidic furin inhibitors suggesting an aminomethyl substitution of this fragment to obtain a couplable P1 residue for the synthesis of substrate-analogue furin inhibitors. The obtained inhibitors possess a slightly improved picomolar inhibitory potency compared to their benzamidine-derived analogues. The crystal structures of two inhibitors in complex with furin revealed that the new P1 group is perfectly suited for incorporation in peptidic furin inhibitors. Selected inhibitors were tested for antiviral activity against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and a furin-dependent influenza A virus (SC35M/H7N7) in A549 human lung cells and demonstrated an efficient inhibition of virus activation and replication at low micromolar or even submicromolar concentrations. First results suggest that the Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor GPCR-X2 could be a potential off-target for certain benzamidine-derived furin inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Philipps University, Marbacher Weg 6-10, D-35032, Marburg, Germany Phone.