Binding and structural studies of the complexes of type 1 ribosome inactivating protein from Momordica balsamina with uracil and uridine.
Pandey, S.N., Iqbal, N., Singh, P.K., Rastogi, N., Kaur, P., Sharma, S., Singh, T.P.(2019) Proteins 87: 99-109
- PubMed: 30007053
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.25584
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
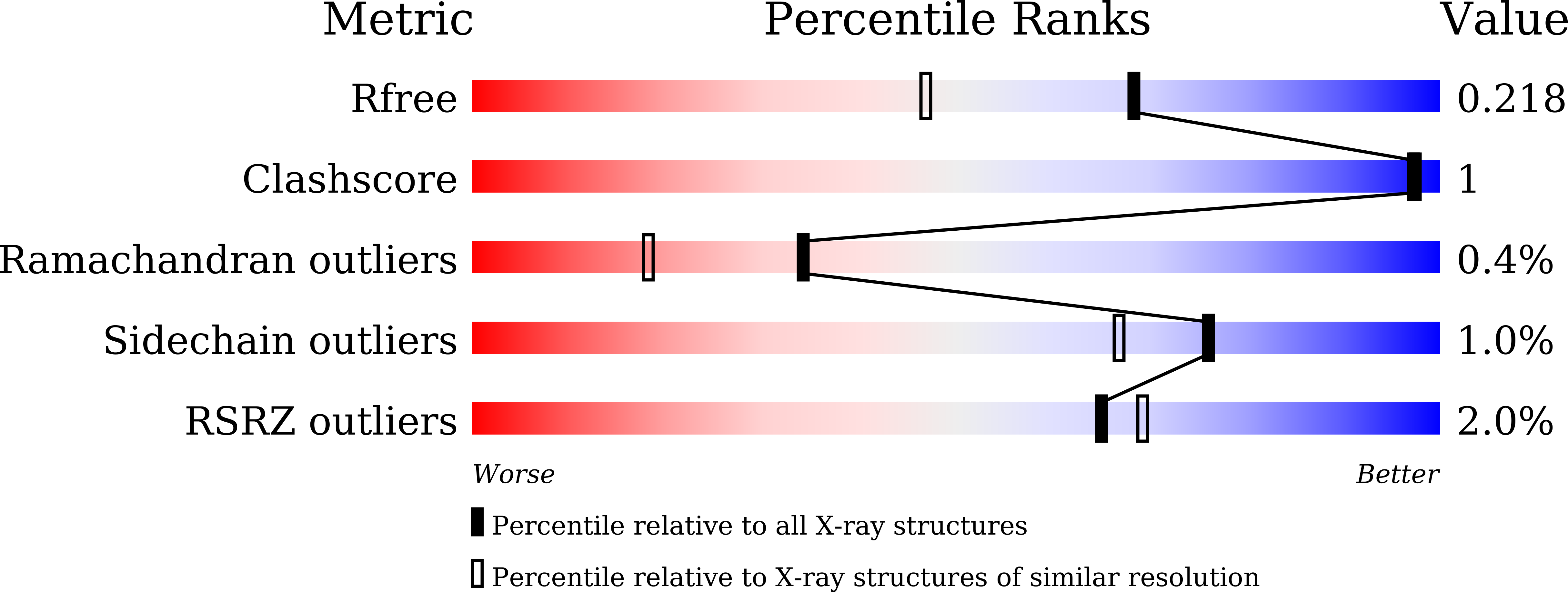
5ILW, 5Y48 - PubMed Abstract:
Ribosome inactivating protein (RIP) catalyzes the cleavage of glycosidic bond formed between adenine and ribose sugar of ribosomal RNA to inactivate ribosomes. Previous structural studies have shown that RNA bases, adenine, guanine, and cytosine tend to bind to RIP in the substrate binding site. However, the mode of binding of uracil with RIP was not yet known. Here, we report crystal structures of two complexes of type 1 RIP from Momordica balsamina (MbRIP1) with base, uracil and nucleoside, uridine. The binding studies of MbRIP1 with uracil and uridine as estimated using fluorescence spectroscopy showed that the equilibrium dissociation constants (K D ) were 1.2?¡Á?10 -6 M and 1.4?¡Á?10 -7 M respectively. The corresponding values obtained using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) were found to be 1.4?¡Á?10 -6 M and 1.1?¡Á?10 -7 M, respectively. Structures of the complexes of MbRIP1 with uracil (Structure-1) and uridine (Structure-2) were determined at 1.70 and 1.98?? resolutions respectively. Structure-1 showed that uracil bound to MbRIP1 at the substrate binding site but its mode of binding was significantly different from those of adenine, guanine and cytosine. However, the mode of binding of uridine was found to be similar to those of cytidine. As a result of binding of uracil to MbRIP1 at the substrate binding site, three water molecules were expelled while eight water molecules were expelled when uridine bound to MbRIP1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India.