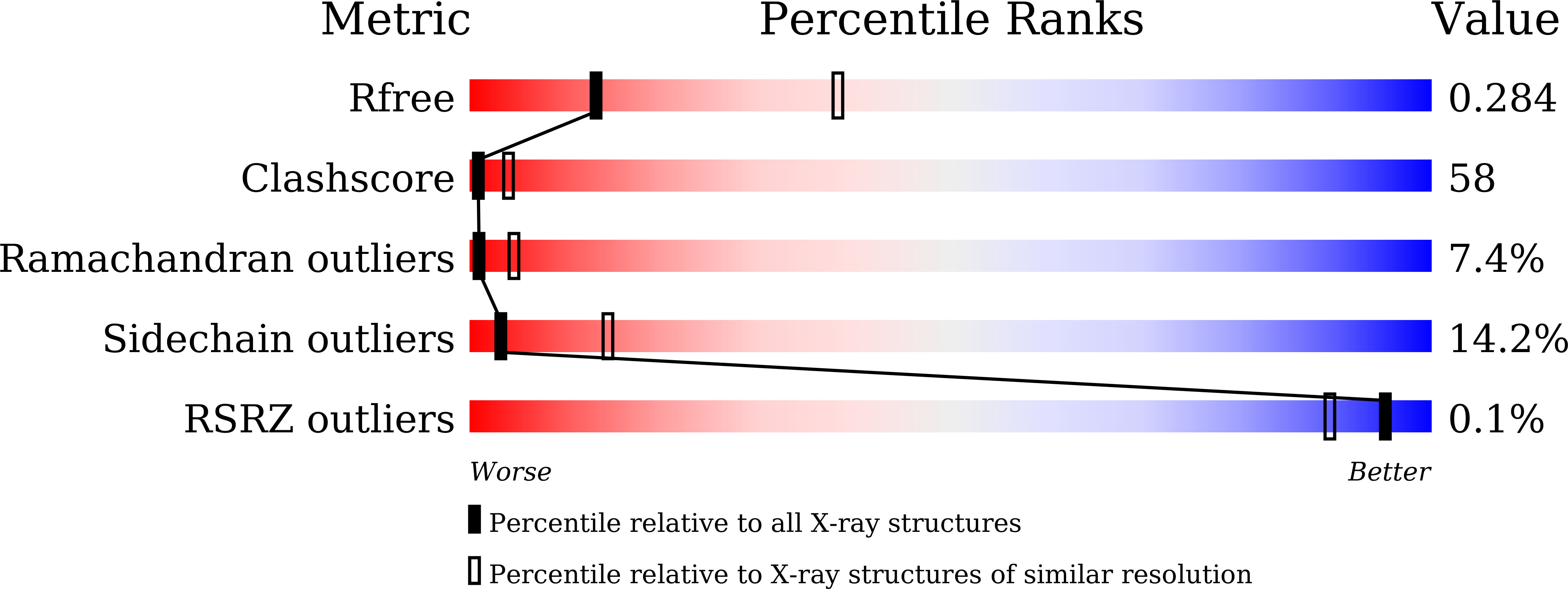
Crystal structures of human serum albumin in complex with lysophosphatidylcholine.
Wang, Y., Luo, Z., Morelli, X., Xu, P., Jiang, L., Shi, X., Huang, M.(2023) Biophys J 122: 4135-4143
- PubMed: 37731243
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2023.09.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ITR, 8ITT - PubMed Abstract:
Lysophospholipids (lysoPLs) are crucial metabolites involved in various physiological and pathological cellular processes. Understanding their binding interactions, particularly with human serum albumin (HSA), is essential due to their role in regulating lysoPLs-induced cytotoxicity. However, the precise mechanism of lysoPLs binding to HSA remains elusive. In this study, we employed fluorescence quenching and optical interferometry assays to demonstrate direct binding between lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) and HSA (K D ?= 25 ¦̀M). Furthermore, we determined crystal structures of HSA in complex with LPC, both in the absence and the presence of the endogenous fatty acid myristate (14:0). The crystal structure of binary HSA:LPC revealed that six LPC molecules are bound to HSA at the primary fatty acid binding sites. Interestingly, the ternary HSA:Myr:LPC structure demonstrated the continued binding of three LPC molecules to HSA at binding sites 1, 3, and 5 in the presence of myristate. These findings support HSA's role as a carrier protein for lysoPLs in blood plasma and provide valuable insights into the structural basis of their binding mechanisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, China; Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Fungi and Mycotoxins of Fujian Province, School of Life Sciences, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China.