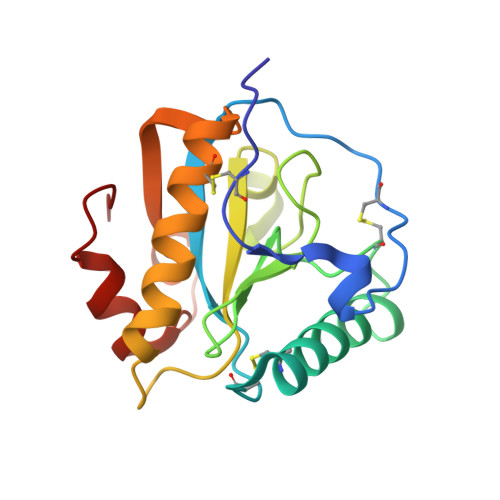
Multiligand specificity of pathogen-associated molecular pattern-binding site in peptidoglycan recognition protein
Sharma, P., Dube, D., Sinha, M., Mishra, B., Dey, S., Mal, G., Pathak, K.M., Kaur, P., Sharma, S., Singh, T.P.(2011) J Biol Chem 286: 31723-31730
- PubMed: 21784863
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.264374
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
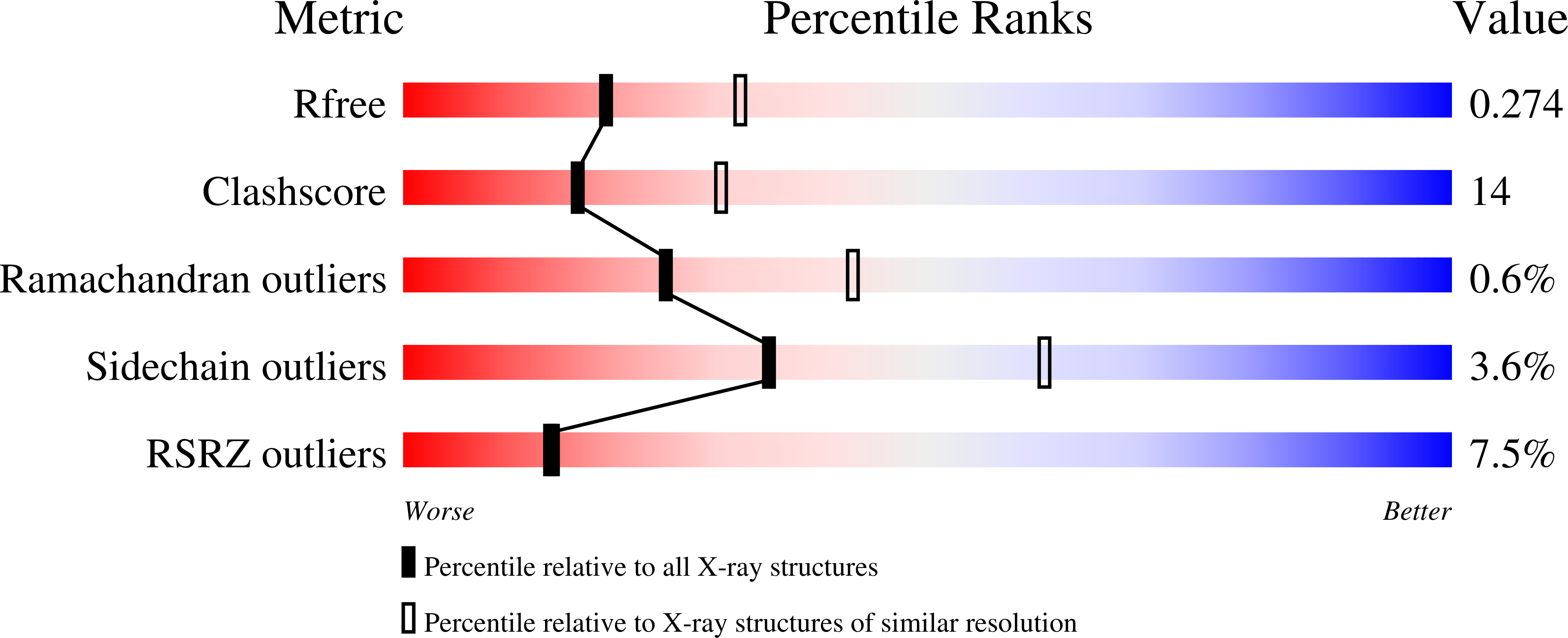
3NG4, 3NW3 - PubMed Abstract:
The peptidoglycan recognition protein PGRP-S is an innate immunity molecule that specifically interacts with microbial peptidoglycans and other pathogen-associated molecular patterns. We report here two structures of the unique tetrameric camel PGRP-S (CPGRP-S) complexed with (i) muramyl dipeptide (MDP) at 2.5 ? resolution and (ii) GlcNAc and ¦Â-maltose at 1.7? resolution. The binding studies carried out using surface plasmon resonance indicated that CPGRP-S binds to MDP with a dissociation constant of 10(-7) M, whereas the binding affinities for GlcNAc and ¦Â-maltose separately are in the range of 10(-4) M to 10(-5) M, whereas the dissociation constant for the mixture of GlcNAc and maltose was estimated to be 10(-6) M. The data from bacterial suspension culture experiments showed a significant inhibition of the growth of Staphylococcus aureus cells when CPGRP-S was added to culture medium. The ELISA experiment showed that the amount of MDP-induced production of TNF-¦Á and IL-6 decreased considerably after the introduction of CPGRP-S. The crystal structure determinations of (i) a binary complex with MDP and (ii) a ternary complex with GlcNAc and ¦Â-maltose revealed that MDP, GlcNAc, and ¦Â-maltose bound to CPGRP-S in the ligand binding cleft, which is situated at the interface of molecules C and D of the homotetramer formed by four protein molecules A, B, C, and D. In the binary complex, the muramyl moiety of MDP is observed at the C-D interface, whereas the peptide chain protrudes into the center of tetramer. In the ternary complex, GlcNAc and ¦Â-maltose occupy distinct non-overlapping positions belonging to different subsites.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India 110029.