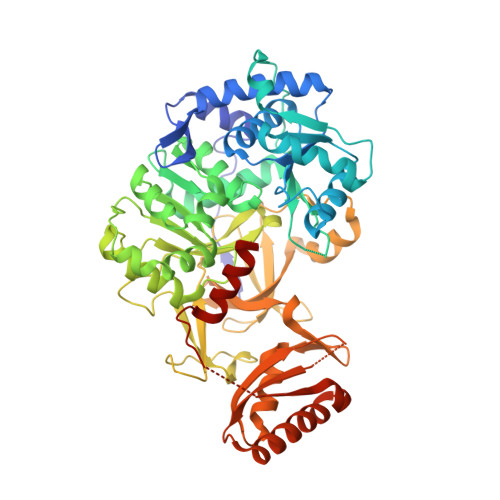
Structural basis of keto acid utilization in nonribosomal depsipeptide synthesis.
Alonzo, D.A., Chiche-Lapierre, C., Tarry, M.J., Wang, J., Schmeing, T.M.(2020) Nat Chem Biol 16: 493-496
- PubMed: 32066969
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-020-0481-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ULW, 6ULX, 6ULY, 6ULZ - PubMed Abstract:
Nonribosomal depsipeptides are natural products composed of amino and hydroxy acid residues. The hydroxy acid residues often derive from ¦Á-keto acids, reduced by ketoreductase domains in the depsipeptide synthetases. Biochemistry and structures reveal the mechanism of discrimination for ¦Á-keto acids and a remarkable architecture: flanking intact adenylation and ketoreductase domains are sequences separated by >1,100 residues that form a split 'pseudoA sub ' domain, structurally important for the depsipeptide module's synthetic cycle.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Centre de Recherche en Biologie Structurale, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.