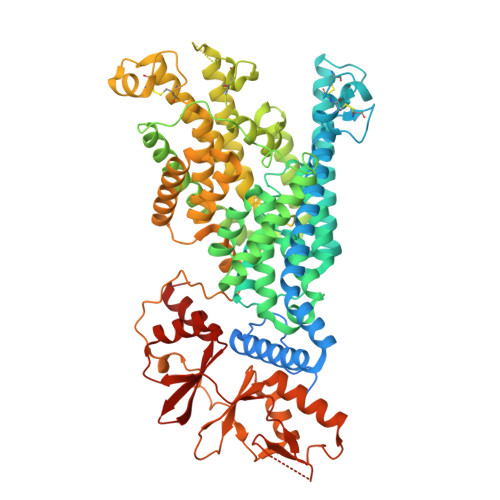
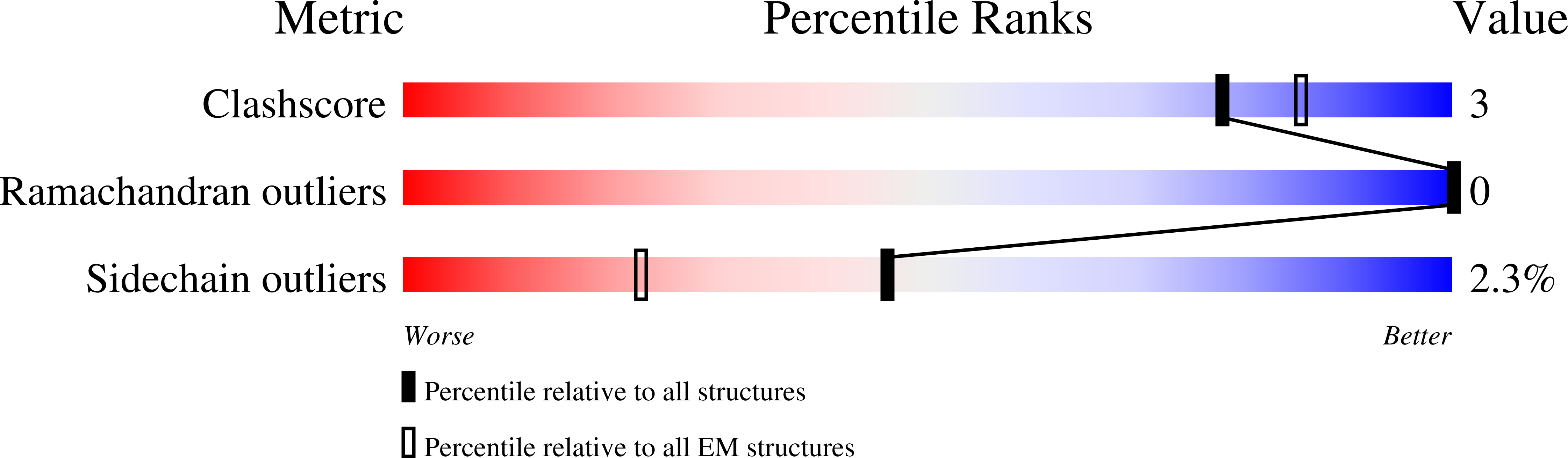Structural basis of ClC-3 inhibition by TMEM9 and PI(3,5)P 2.
Schrecker, M., Son, Y., Planells-Cases, R., Kar, S., Vorobeva, V., Schulte, U., Fakler, B., Jentsch, T.J., Hite, R.K.(2025) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 40093093
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.02.28.640562
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9DNW, 9DNX, 9DNY, 9DNZ, 9DO0 - PubMed Abstract:
The trafficking and activity of endosomes relies on the exchange of chloride ions and protons by members of the CLC family of chloride channels and transporters, whose mutations are associated with numerous diseases. Despite their critical roles, the mechanisms by which CLC transporters are regulated are poorly understood. Here, we show that two related accessory ¦Â-subunits, TMEM9 and TMEM9B, directly interact with ClC-3, -4 and -5. Cryo-EM structures reveal that TMEM9 inhibits ClC-3 by sealing the cytosolic entrance to the Cl - ion pathway. Unexpectedly, we find that PI(3,5)P 2 stabilizes the interaction between TMEM9 and ClC-3 and is required for proper regulation of ClC-3 by TMEM9. Collectively, our findings reveal that TMEM9 and PI(3,5)P 2 collaborate to regulate endosomal ion homeostasis by modulating the activity of ClC-3.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center; New York, NY, USA.