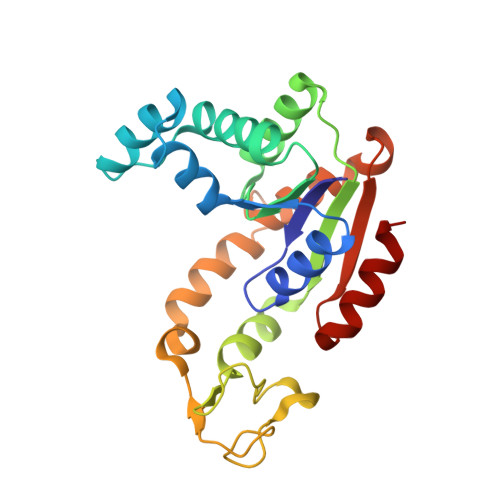
Crystal structure of the zinc-, cobalt-, and iron-containing adenylate kinase from Desulfovibrio gigas: a novel metal-containing adenylate kinase from Gram-negative bacteria
Mukhopadhyay, A., Kladova, A.V., Bursakov, S.A., Gavel, O.Y., Calvete, J.J., Shnyrov, V.L., Moura, I., Moura, J.J.G., Romao, M.J., Trincao, J.(2011) J Biol Inorg Chem 16: 51-61
- PubMed: 20821240
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-010-0700-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XB4, 3L0P, 3L0S - PubMed Abstract:
Adenylate kinases (AK) from Gram-negative bacteria are generally devoid of metal ions in their LID domain. However, three metal ions, zinc, cobalt, and iron, have been found in AK from Gram-negative bacteria. Crystal structures of substrate-free AK from Desulfovibrio gigas with three different metal ions (Zn(2+), Zn-AK; Co(2+), Co-AK; and Fe(2+), Fe-AK) bound in its LID domain have been determined by X-ray crystallography to resolutions 1.8, 2.0, and 3.0??, respectively. The zinc and iron forms of the enzyme were crystallized in space group I222, whereas the cobalt-form crystals were C2. The presence of the metals was confirmed by calculation of anomalous difference maps and by X-ray fluorescence scans. The work presented here is the first report of a structure of a metal-containing AK from a Gram-negative bacterium. The native enzyme was crystallized, and only zinc was detected in the LID domain. Co-AK and Fe-AK were obtained by overexpressing the protein in Escherichia coli. Zn-AK and Fe-AK crystallized as monomers in the asymmetric unit, whereas Co-AK crystallized as a dimer. Nevertheless, all three crystal structures are very similar to each other, with the same LID domain topology, the only change being the presence of the different metal atoms. In the absence of any substrate, the LID domain of all holoforms of AK was present in a fully open conformational state. Normal mode analysis was performed to predict fluctuations of the LID domain along the catalytic pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
REQUIMTE, Departamento de Qu¨ªmica, Centro de Qu¨ªmica Fina e Biotecnologia, Faculdade de Ci¨ºncias e Tecnologia, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Caparica, Portugal.