Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor Gamma is a target for halogenated analogs of bisphenol A.
Riu, A., Grimaldi, M., le Maire, A., Bey, G., Phillips, K., Boulahtouf, A., Perdu, E., Zalko, D., Bourguet, W., Balaguer, P.(2011) Environ Health Perspect 119: 1227-1232
- PubMed: 21561829
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1003328
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
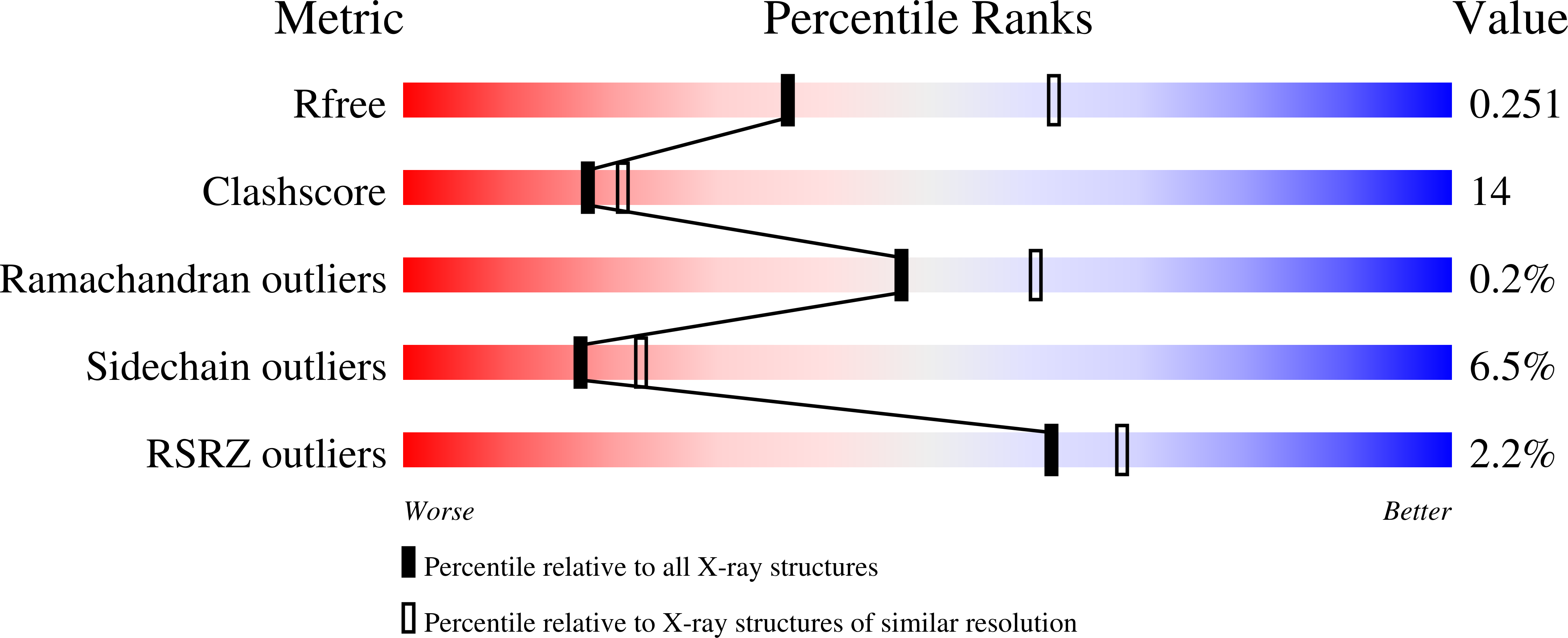
3OSI, 3OSW - PubMed Abstract:
The occurrence of halogenated analogs of the xenoestrogen bisphenol A (BPA) has been recently demonstrated both in environmental and human samples. These analogs include brominated [e.g., tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA)] and chlorinated [e.g., tetrachlorobisphenol A (TCBPA)] bisphenols, which are both flame retardants. Because of their structural homology with BPA, such chemicals are candidate endocrine disruptors. However, their possible target(s) within the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily has remained unknown. We investigated whether BPA and its halogenated analogs could be ligands of estrogen receptors (ERs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and act as endocrine-disrupting chemicals. We studied the activity of compounds using reporter cell lines expressing ERs and PPARs. We measured the binding affinities to PPARŽ├ by competitive binding assays with [3H]-rosiglitazone and investigated the impact of TBBPA and TCBPA on adipocyte differentiation using NIH3T3-L1 cells. Finally, we determined the binding mode of halogenated BPAs to PPARŽ├ by X-ray crystallography. We observed that TBBPA and TCBPA are human, zebrafish, and Xenopus PPARŽ├ ligands and determined the mechanism by which these chemicals bind to and activate PPARŽ├. We also found evidence that activation of ERŽ┴, ERŽ┬, and PPARŽ├ depends on the degree of halogenation in BPA analogs. We observed that the bulkier brominated BPA analogs, the greater their capability to activate PPARŽ├ and the weaker their estrogenic potential. Our results strongly suggest that polyhalogenated bisphenols could function as obesogens by acting as agonists to disrupt physiological functions regulated by human or animal PPARŽ├.
Organizational Affiliation:
INRA (National Institute of Agronomic Research), UMR 1089 XĘŽnobiotiques, Toulouse, France.