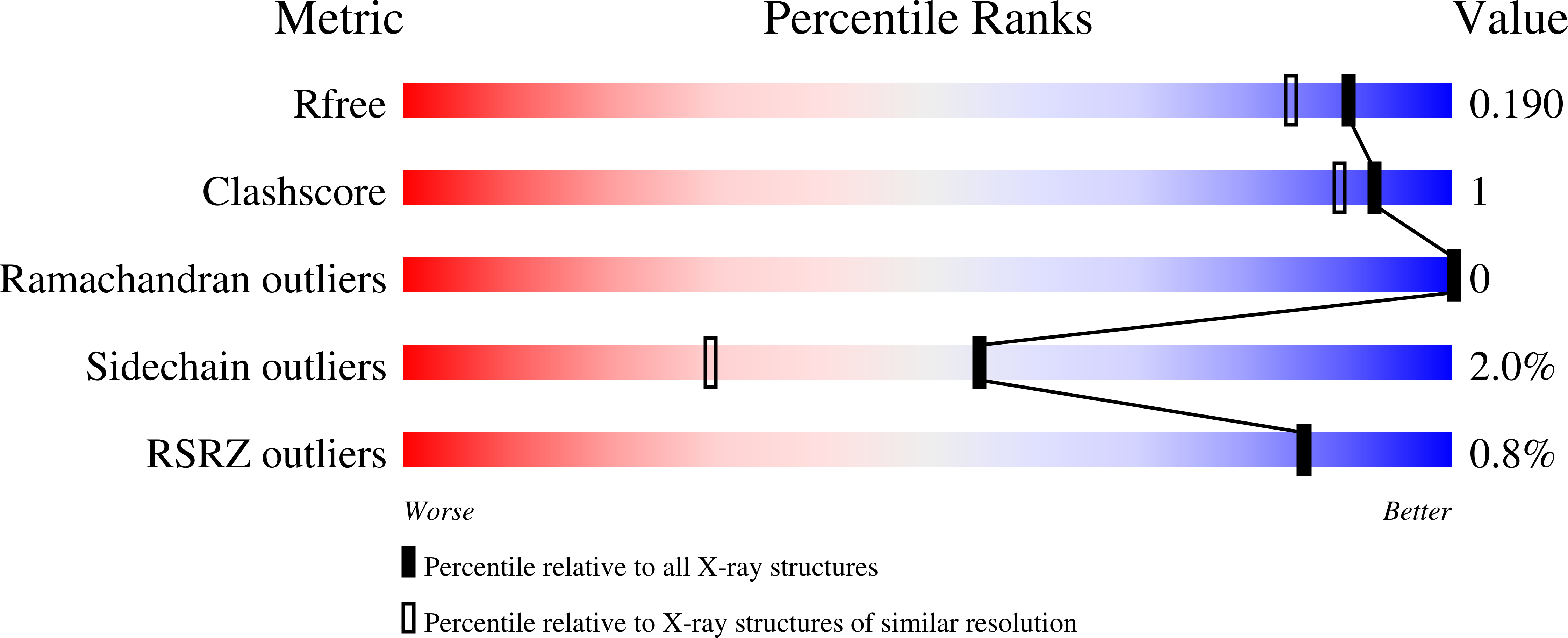
Crystal structures of KPC-2 {beta}-lactamase in complex with 3-nitrophenyl boronic acid and the penam sulfone PSR-3-226.
Ke, W., Bethel, C.R., Papp-Wallace, K.M., Pagadala, S.R., Nottingham, M., Fernandez, D., Buynak, J.D., Bonomo, R.A., van den Akker, F.(2012) Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56: 2713-2718
- PubMed: 22330909
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.06099-11
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RXW, 3RXX - PubMed Abstract:
Class A carbapenemases are a major threat to the potency of carbapenem antibiotics. A widespread carbapenemase, KPC-2, is not easily inhibited by ¦Â-lactamase inhibitors (i.e., clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam). To explore different mechanisms of inhibition of KPC-2, we determined the crystal structures of KPC-2 with two ¦Â-lactamase inhibitors that follow different inactivation pathways and kinetics. The first complex is that of a small boronic acid compound, 3-nitrophenyl boronic acid (3-NPBA), bound to KPC-2 with 1.62-? resolution. 3-NPBA demonstrated a K(m) value of 1.0 ¡À 0.1 ¦ÌM (mean ¡À standard error) for KPC-2 and blocks the active site by making a reversible covalent interaction with the catalytic S70 residue. The two boron hydroxyl atoms of 3-NPBA are positioned in the oxyanion hole and the deacylation water pocket, respectively. In addition, the aromatic ring of 3-NPBA provides an edge-to-face interaction with W105 in the active site. The structure of KPC-2 with the penam sulfone PSR-3-226 was determined at 1.26-? resolution. PSR-3-226 displayed a K(m) value of 3.8 ¡À 0.4 ¦ÌM for KPC-2, and the inactivation rate constant (k(inact)) was 0.034 ¡À 0.003 s(-1). When covalently bound to S70, PSR-3-226 forms a trans-enamine intermediate in the KPC-2 active site. The predominant active site interactions are generated via the carbonyl oxygen, which resides in the oxyanion hole, and the carboxyl moiety of PSR-3-226, which interacts with N132, N170, and E166. 3-NPBA and PSR-3-226 are the first ¦Â-lactamase inhibitors to be trapped as an acyl-enzyme complex with KPC-2. The structural and inhibitory insights gained here could aid in the design of potent KPC-2 inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departments of Biochemistry, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, USA.