Ligand Binding Mechanism in Steroid Receptors: From Conserved Plasticity to Differential Evolutionary Constraints.
Edman, K., Hosseini, A., Bjursell, M.K., Aagaard, A., Wissler, L., Gunnarsson, A., Kaminski, T., Kohler, C., Backstrom, S., Jensen, T.J., Cavallin, A., Karlsson, U., Nilsson, E., Lecina, D., Takahashi, R., Grebner, C., Geschwindner, S., Lepisto, M., Hogner, A.C., Guallar, V.(2015) Structure 23: 2280
- PubMed: 26602186
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.09.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4UDA, 4UDB, 4UDC, 4UDD - PubMed Abstract:
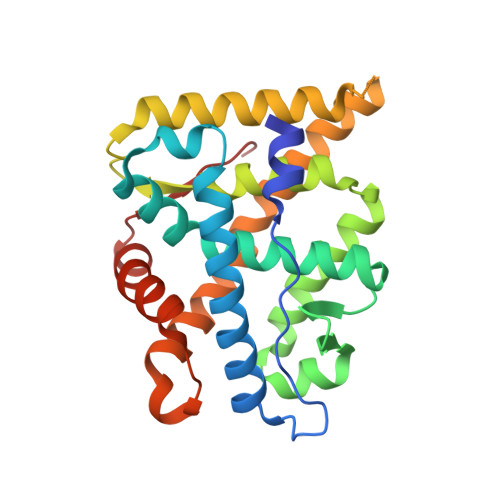
Steroid receptor drugs have been available for more than half a century, but details of the ligand binding mechanism have remained elusive. We solved X-ray structures of the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors to identify a conserved plasticity at the helix 6-7 region that extends the ligand binding pocket toward the receptor surface. Since none of the endogenous ligands exploit this region, we hypothesized that it constitutes an integral part of the binding event. Extensive all-atom unbiased ligand exit and entrance simulations corroborate a ligand binding pathway that gives the observed structural plasticity a key functional role. Kinetic measurements reveal that the receptor residence time correlates with structural rearrangements observed in both structures and simulations. Ultimately, our findings reveal why nature has conserved the capacity to open up this region, and highlight how differences in the details of the ligand entry process result in differential evolutionary constraints across the steroid receptors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Discovery Sciences, AstraZeneca, M?lndal, Pepparedsleden 1, 43183 M?lndal, Sweden. Electronic address: karl.edman@astrazeneca.com.