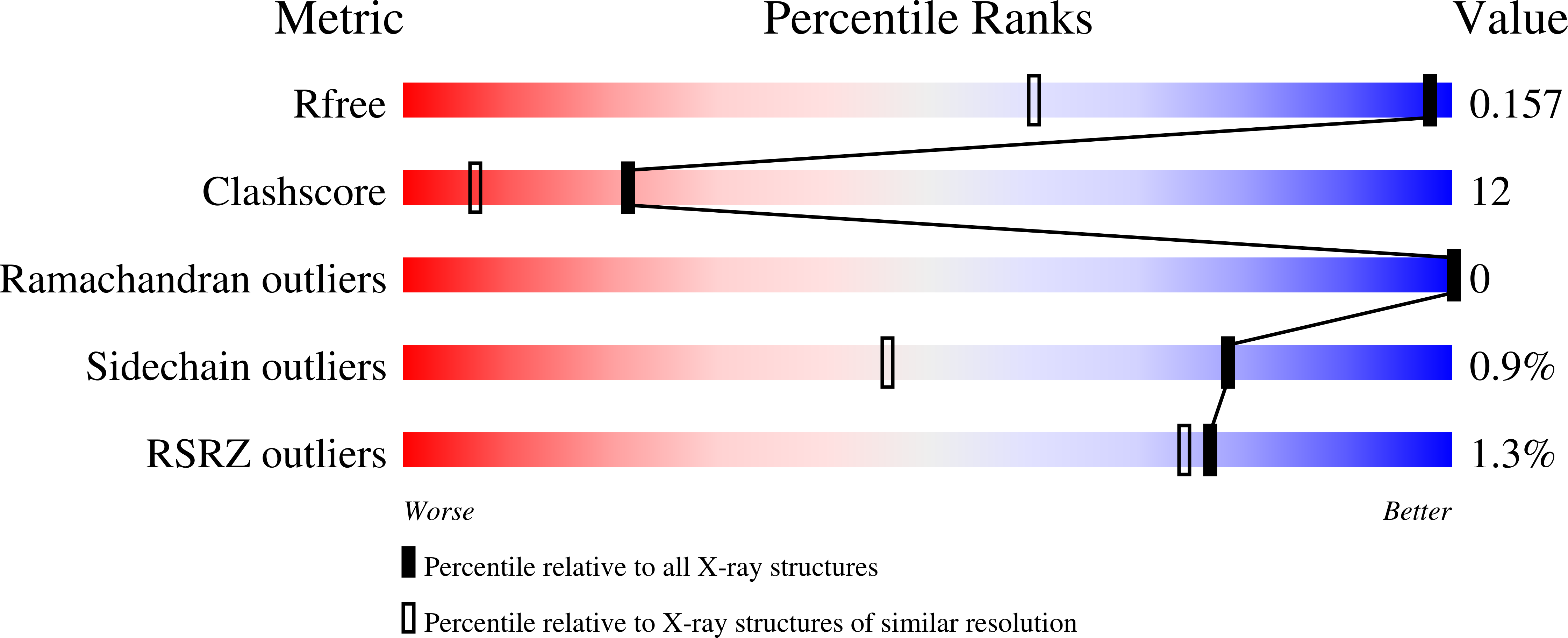
The catalytic mechanism and unique low pH optimum of Caldicellulosiruptor bescii family 3 pectate lyase.
Alahuhta, M., Taylor, L.E., Brunecky, R., Sammond, D.W., Michener, W., Adams, M.W., Himmel, M.E., Bomble, Y.J., Lunin, V.(2015) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 71: 1946-1954
- PubMed: 26327384
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004715013760
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4YZ0, 4YZA, 4YZQ, 4YZX, 4Z03, 4Z05, 4Z06 - PubMed Abstract:
The unique active site of the Caldicellulosiruptor bescii family 3 pectate lyase (PL3) enzyme has been thoroughly characterized using a series of point mutations, X-ray crystallography, pK(a) calculations and biochemical assays. The X-ray structures of seven PL3 active-site mutants, five of them in complex with intact trigalacturonic acid, were solved and characterized structurally, biochemically and computationally. The results confirmed that Lys108 is the catalytic base, but there is no clear candidate for the catalytic acid. However, the reaction mechanism can also be explained by an antiperiplanar trans-elimination reaction, in which Lys108 abstracts a proton from the C5 atom without the help of simultaneous proton donation by an acidic residue. An acidified water molecule completes the anti ¦Â-elimination reaction by protonating the O4 atom of the substrate. Both the C5 hydrogen and C4 hydroxyl groups of the substrate must be orientated in axial configurations, as for galacturonic acid, for this to be possible. The wild-type C. bescii PL3 displays a pH optimum that is lower than that of Bacillus subtilis PL1 according to activity measurements, indicating that C. bescii PL3 has acquired a lower pH optimum by utilizing lysine instead of arginine as the catalytic base, as well as by lowering the pK(a) of the catalytic base in a unique active-site environment.
Organizational Affiliation:
BioSciences Center, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, 15013 Denver West Parkway, Golden, CO 80401, USA.