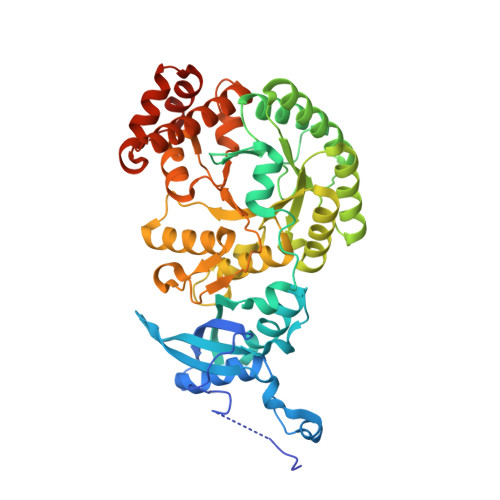
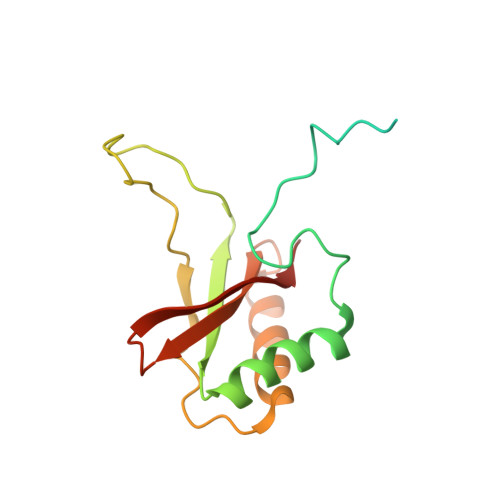
Hybrid Rubisco with Complete Replacement of Rice Rubisco Small Subunits by Sorghum Counterparts Confers C 4 Plant-like High Catalytic Activity.
Matsumura, H., Shiomi, K., Yamamoto, A., Taketani, Y., Kobayashi, N., Yoshizawa, T., Tanaka, S.I., Yoshikawa, H., Endo, M., Fukayama, H.(2020) Mol Plant 13: 1570-1581
- PubMed: 32882392
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.08.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6KYI, 6KYJ - PubMed Abstract:
Photosynthetic rate at the present atmospheric condition is limited by the CO 2 -fixing enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) because of its extremely low catalytic rate (k cat ) and poor affinity for CO 2 (K c ) and specificity for CO 2 (S c/o ). Rubisco in C 4 plants generally shows higher k cat than that in C 3 plants. Rubisco consists of eight large subunits and eight small subunits (RbcS). Previously, the chimeric incorporation of sorghum C 4 -type RbcS significantly increased the k cat of Rubisco in a C 3 plant, rice. In this study, we knocked out rice RbcS multigene family using the CRISPR-Cas9 technology and completely replaced rice RbcS with sorghum RbcS in rice Rubisco. Obtained hybrid Rubisco showed almost C 4 plant-like catalytic properties, i.e., higher k cat , higher K c , and lower S c/o . Transgenic lines expressing the hybrid Rubisco accumulated reduced levels of Rubisco, whereas they showed slightly but significantly higher photosynthetic capacity and similar biomass production under high CO 2 condition compared with wild-type rice. High-resolution crystal structural analysis of the wild-type Rubisco and hybrid Rubisco revealed the structural differences around the central pore of Rubisco and the ¦ĀC-¦ĀD hairpin in RbcS. We propose that such differences, particularly in the ¦ĀC-¦ĀD hairpin, may impact the flexibility of Rubisco catalytic site and change its catalytic properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biotechnology, College of Life Sciences, Ritsumeikan University, 1-1-1 Noji-Higashi, Kusatsu 525-8577, Japan. Electronic address: h-matsu@fc.ritsumei.ac.jp.