A unique clade of light-driven proton-pumping rhodopsins evolved in the cyanobacterial lineage.
Hasegawa, M., Hosaka, T., Kojima, K., Nishimura, Y., Nakajima, Y., Kimura-Someya, T., Shirouzu, M., Sudo, Y., Yoshizawa, S.(2020) Sci Rep 10: 16752-16752
- PubMed: 33028840
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73606-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LM0, 6LM1 - PubMed Abstract:
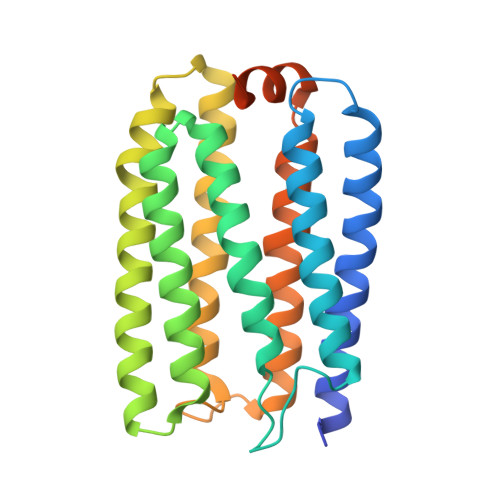
Microbial rhodopsin is a photoreceptor protein found in various bacteria and archaea, and it is considered to be a light-utilization device unique to heterotrophs. Recent studies have shown that several cyanobacterial genomes also include genes that encode rhodopsins, indicating that these auxiliary light-utilizing proteins may have evolved within photoautotroph lineages. To explore this possibility, we performed a large-scale genomic survey to clarify the distribution of rhodopsin and its phylogeny. Our surveys revealed a novel rhodopsin clade, cyanorhodopsin (CyR), that is unique to cyanobacteria. Genomic analysis revealed that rhodopsin genes show a habitat-biased distribution in cyanobacterial taxa, and that the CyR clade is composed exclusively of non-marine cyanobacterial strains. Functional analysis using a heterologous expression system revealed that CyRs function as light-driven outward H + pumps. Examination of the photochemical properties and crystal structure (2.65?? resolution) of a representative CyR protein, N2098R from Calothrix sp. NIES-2098, revealed that the structure of the protein is very similar to that of other rhodopsins such as bacteriorhodopsin, but that its retinal configuration and spectroscopic characteristics (absorption maximum and photocycle) are distinct from those of bacteriorhodopsin. These results suggest that the CyR clade proteins evolved together with chlorophyll-based photosynthesis systems and may have been optimized for the cyanobacterial environment.
Organizational Affiliation:
Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, The University of Tokyo, Chiba, 277-8564, Japan.