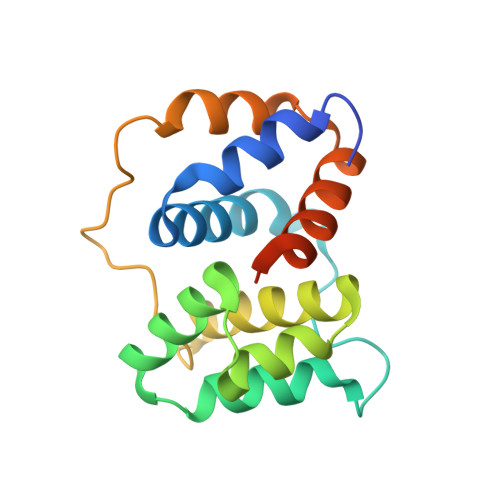
Structural and spectroscopic characterization of HCP2.
Dominguez-Martin, M.A., Polivka, T., Sutter, M., Ferlez, B., Lechno-Yossef, S., Montgomery, B.L., Kerfeld, C.A.(2019) Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1860: 414-424
- PubMed: 30880081
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2019.03.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6MCJ - PubMed Abstract:
The Helical Carotenoid Proteins (HCPs) are a large group of newly identified carotenoid-binding proteins found in ecophysiologically diverse cyanobacteria. They likely evolved before becoming the effector (quenching) domain of the modular Orange Carotenoid Protein (OCP). The number of discrete HCP families-at least nine-suggests they are involved in multiple distinct functions. Here we report the 1.7?? crystal structure of HCP2, one of the most widespread HCPs found in nature, from the chromatically acclimating cyanobacterium Tolypothrix sp. PCC 7601. By purifying HCP2 from the native source we are able to identify its natively-bound carotenoid, which is exclusively canthaxanthin. In solution, HCP2 is a monomer with an absorbance maximum of 530?nm. However, the HCP2 crystals have a maximum absorbance at 548?nm, which is accounted by the stacking of the ¦Â1 rings of the carotenoid in the two molecules in the asymmetric unit. Our results demonstrate how HCPs provide a valuable system to study carotenoid-protein interactions and their spectroscopic implications, and contribute to efforts to understand the functional roles of this large, newly discovered family of pigment proteins, which to-date remain enigmatic.
Organizational Affiliation:
MSU-DOE Plant Research Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA.