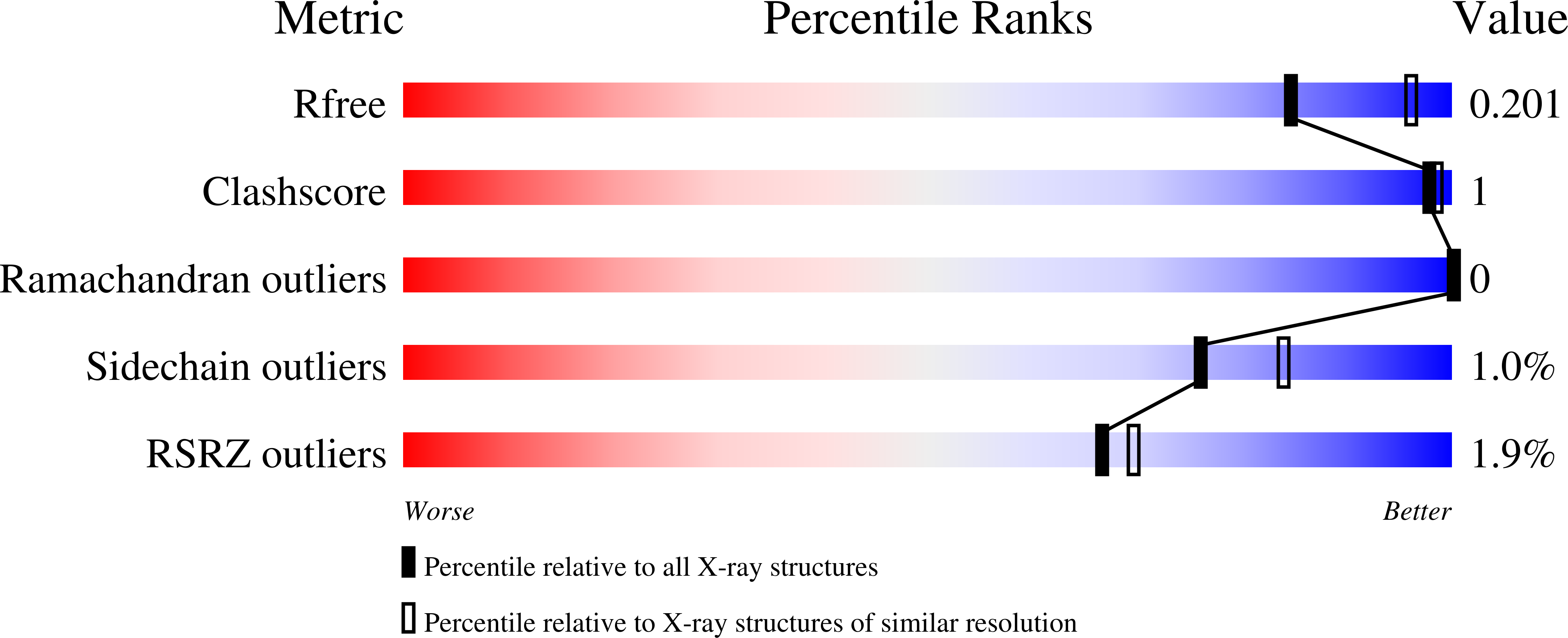
Cholera toxin B scaffolded, focused SIV V2 epitope elicits antibodies that influence the risk of SIV mac251 acquisition in macaques.
Rahman, M.A., Becerra-Flores, M., Patskovsky, Y., Silva de Castro, I., Bissa, M., Basu, S., Shen, X., Williams, L.D., Sarkis, S., N'guessan, K.F., LaBranche, C., Tomaras, G.D., Aye, P.P., Veazey, R., Paquin-Proulx, D., Rao, M., Franchini, G., Cardozo, T.(2023) Front Immunol 14: 1139402-1139402
- PubMed: 37153584
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1139402
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LVB - PubMed Abstract:
An efficacious HIV vaccine will need to elicit a complex package of innate, humoral, and cellular immune responses. This complex package of responses to vaccine candidates has been studied and yielded important results, yet it has been a recurring challenge to determine the magnitude and protective effect of specific in vivo immune responses in isolation. We therefore designed a single, viral-spike-apical, epitope-focused V2 loop immunogen to reveal individual vaccine-elicited immune factors that contribute to protection against HIV/SIV. We generated a novel vaccine by incorporating the V2 loop B-cell epitope in the cholera toxin B (CTB) scaffold and compared two new immunization regimens to a historically protective 'standard' vaccine regimen (SVR) consisting of 2xDNA prime boosted with 2xALVAC-SIV and 1x¦¤V1gp120. We immunized a cohort of macaques with 5xCTB-V2c vaccine+alum intramuscularly simultaneously with topical intrarectal vaccination of CTB-V2c vaccine without alum (5xCTB-V2/alum). In a second group, we tested a modified version of the SVR consisting of 2xDNA prime and boosted with 1xALVAC-SIV and 2xALVAC-SIV+CTB-V2/alum, (DA/CTB-V2c/alum). In the absence of any other anti-viral antibodies, V2c epitope was highly immunogenic when incorporated in the CTB scaffold and generated highly functional anti-V2c antibodies in the vaccinated animals. 5xCTB-V2c/alum vaccination mediated non-neutralizing ADCC activity and efferocytosis, but produced low avidity, trogocytosis, and no neutralization of tier 1 virus. Furthermore, DA/CTB-V2c/alum vaccination also generated lower total ADCC activity, avidity, and neutralization compared to the SVR. These data suggest that the ¦¤V1gp120 boost in the SVR yielded more favorable immune responses than its CTB-V2c counterpart. Vaccination with the SVR generates CCR5 - ¦Á4¦Â7 + CD4 + Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells, which are less likely to be infected by SIV/HIV and likely contributed to the protection afforded in this regimen. The 5xCTB-V2c/alum regimen likewise elicited higher circulating CCR5 - ¦Á4¦Â7 + CD4 + T cells and mucosal ¦Á4¦Â7 + CD4 + T cells compared to the DA/CTB-V2c/alum regimen, whereas the first cell type was associated with reduced risk of viral acquisition. Taken together, these data suggest that individual viral spike B-cell epitopes can be highly immunogenic and functional as isolated immunogens, although they might not be sufficient on their own to provide full protection against HIV/SIV infection.
Organizational Affiliation:
Animal Models and Retroviral Vaccines Section, National Cancer Institute, NIH Bethesda, MD, United States.