Human glutathione transferases catalyze the reaction between glutathione and nitrooleic acid.
Steglich, M., Larrieux, N., Zeida, A., Rizza, J.D., Salvatore, S.R., Bonilla, M., Moller, M.N., Buschiazzo, A., Alvarez, B., Schopfer, F.J., Turell, L.(2025) J Biological Chem : 108362-108362
- PubMed: 40024478
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108362
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
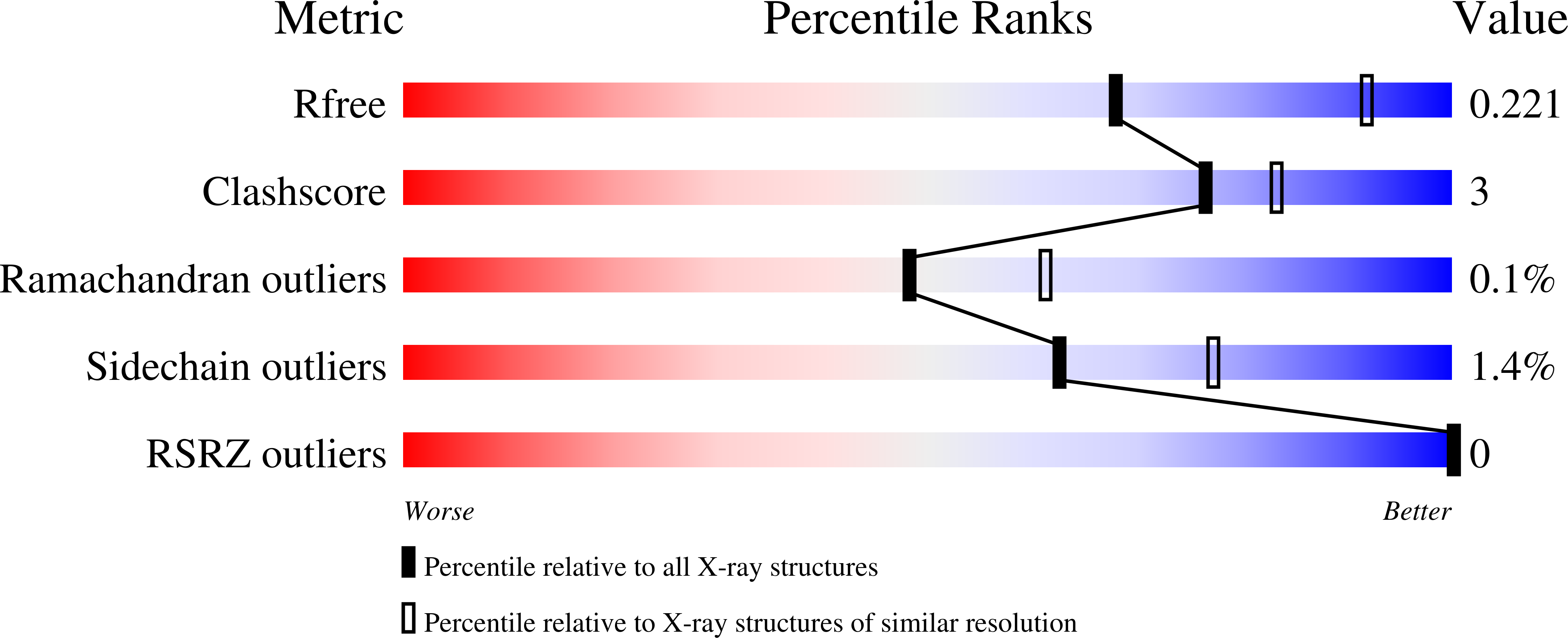
8VOU - PubMed Abstract:
Nitroalkene fatty acids (NO 2 -FAs) are formed endogenously. They regulate cell signaling pathways and are being developed clinically to treat inflammatory diseases. NO 2 -FAs are electrophilic and form thioether adducts with glutathione (GSH), which are exported from cells. Glutathione transferases (GSTs), a superfamily of enzymes, contribute to the cellular detoxification of hydrophobic electrophiles by catalyzing their conjugation to GSH. Herein, we evaluated the capacity of five human GSTs (M1-1, M2-2, M4-4, A4-4, and P1-1) to catalyze the reaction between nitrooleic acid (NO 2 -OA) and GSH. The reaction was monitored by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and catalytic activity was detected with hGSTs M1-1 and A4-4. Using stopped-flow spectrophotometry, a 1400 and 7500-fold increase in the apparent second-order rate constant was observed for hGST M1-1 and hGST A4-4, respectively, compared to the uncatalyzed reaction (pH 7.4, 25 ¡ãC), in part due to a higher availability of the thiolate. The crystal structure of hGST M1-1 in complex with the adduct was solved at 2.55 ? resolution, revealing that the ligand was bound within the reaction center, and establishing a foundation to build a model of hGST A4-4 in complex with the adduct. A larger number of interactions between the enzyme and the fatty acid were observed for hGST A4-4 compared to hGST M1-1, probably contributing to the increased catalysis. Altogether, these results show, for the first time, that hGSTs can catalyze the reaction between GSH and NO 2 -FAs, likely affecting the signaling actions of these metabolites and expanding the repertoire of GST reactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratorio de Enzimolog¨ªa, Instituto de Qu¨ªmica Biol¨®gica, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de la Rep¨²blica, Uruguay; Centro de Investigaciones Biom¨¦dicas (CEINBIO), Universidad de la Rep¨²blica, Uruguay; Graduate Program in Chemistry, Facultad de Qu¨ªmica, Universidad de la Rep¨²blica, Uruguay.