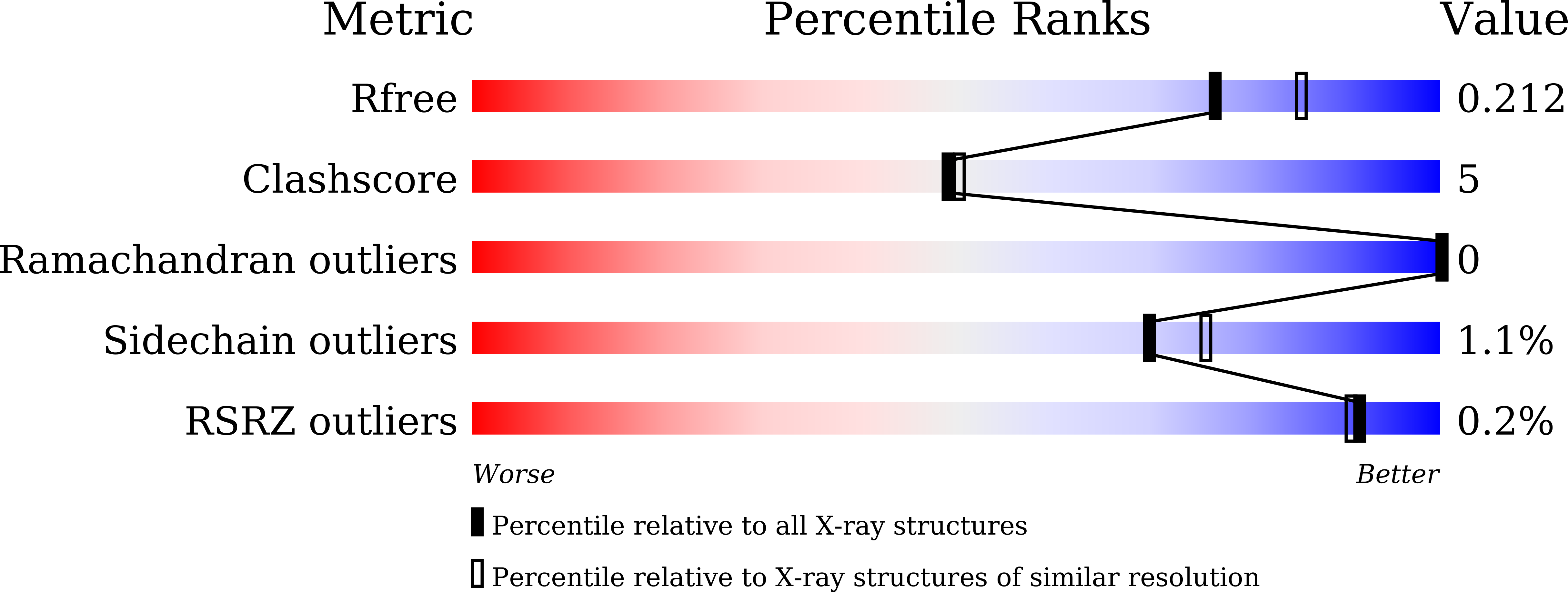
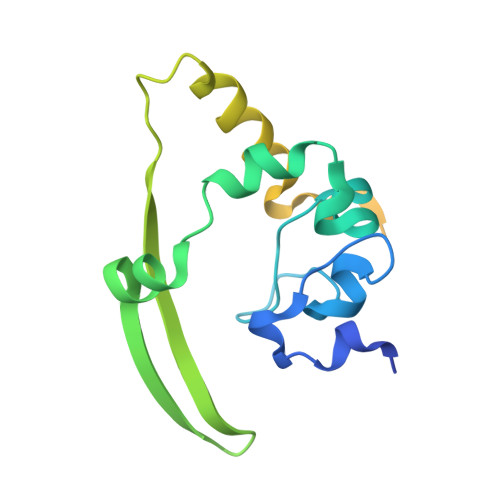
Structural insights into the RNA binding inhibitors of the C-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid.
Dhaka, P., Mahto, J.K., Singh, A., Kumar, P., Tomar, S.(2025) J Struct Biol 217: 108197-108197
- PubMed: 40113149
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2025.108197
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8W6W, 8ZFV, 9IN1 - PubMed Abstract:
The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein is an essential structural element of the virion, playing a crucial role in enclosing the viral genome into a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) assembly, as well as viral replication and transmission. The C-terminal domain of the N-protein (N-CTD) is essential for encapsidation, contributing to the stabilization of the RNP complex. In a previous study, three inhibitors (ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, and ampicillin) were screened for their potential to disrupt the RNA packaging process by targeting the N-protein. However, the binding efficacy, mechanism of RNA binding inhibition, and molecular insights of binding with N-CTD remain unclear. In this study, we evaluated the binding efficacy of these inhibitors using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), revealing the affinity of ceftriaxone (18?¡À?1.3?¦ÌM), cefuroxime (55?¡À?4.2?¦ÌM), and ampicillin (28?¡À?1.2?¦ÌM) with the N-CTD. Further inhibition assay and fluorescence polarisation assay demonstrated RNA binding inhibition, with IC 50 ranging from?¡«?12 to 18?¦ÌM and K D values between 24?¦ÌM to 32?¦ÌM for the inhibitors, respectively. Additionally, we also determined the inhibitor-bound complex crystal structures of N-CTD-Ceftriaxone (2.0 ?) and N-CTD-Ampicillin (2.2 ?), along with the structure of apo N-CTD (1.4 ?). These crystal structures revealed previously unobserved interaction sites involving residues K261, K266, R293, Q294, and W301 at the oligomerization interface and the predicted RNA-binding region of N-CTD. These findings provide valuable molecular insights into the inhibition of N-CTD, highlighting its potential as an underexplored but promising target for the development of novel antiviral agents against coronaviruses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee, Uttarakhand 247667, India.