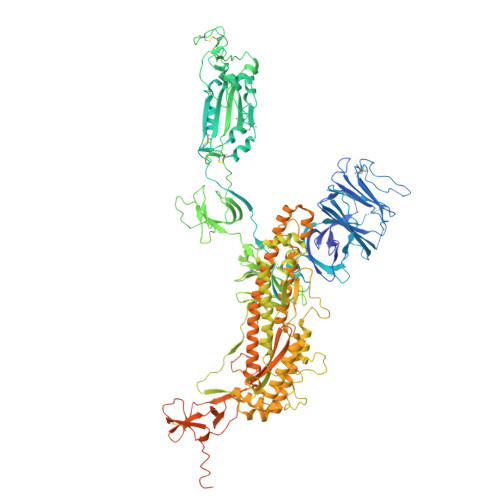
Structure and dynamics of Alpha B.1.1.7 SARS-CoV-2 S-protein in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody REGN10987.
Kocharovskaya, M.V., Pichkur, E.B., Ivannikov, A.D., Kharlampieva, D.D., Grafskaia, E.N., Lyukmanova, E.N., Kirpichnikov, M.P., Shenkarev, Z.O.(2025) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 755: 151558-151558
- PubMed: 40043614
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151558
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9LYO, 9LYP - PubMed Abstract:
One of the approaches for treatment of COVID-19 is a use of neutralizing antibodies (nAbs). The study of the mechanisms by which nAbs recognize different strains of SARS-CoV-2 may facilitate the development of new drugs and vaccines against the coronavirus infection. In this work, we present the 3.1?? resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of a full-length trimeric spike-protein (S-protein) of the SARS-CoV-2 Alpha (B.1.1.7) variant in complex with the Fab of the REGN10987 nAb. In the complex, two receptor-binding domains (RBDs) of the S-protein were observed in the 'up' state, whereas third RBD was in the 'down' state. This distinguishes the obtained structure from the complex of Delta (B.1.617.2) S-protein with REGN10987-Fab, where only one RBD was in the 'up' state. Probably some of the substituted residues (K478T, A570D, and S982A) located at the interprotomer interfaces are responsible for the greater Alpha S-protein opening upon the REGN10987-Fab binding. The Fab identically binds to the RBD in the both 'up' and 'down' conformations. The RBD-Fab interaction interface was refined to a resolution of 3.6??. The antibody binds to the receptor-binding motif (RBM), which prevents the S-protein from the binding to its receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2). Comparison with the structures of the Wuhan (wild type) and Delta RBD variants in complex with REGN10987-Fab revealed that the N501Y and T478K/L452R mutations presented in the RBM of the Alpha and Delta variants, respectively, do not affect the mode of the RBD-Fab interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Shemyakin-Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, 117997, Moscow, Russia; Moscow Center for Advanced Studies, 123592, Moscow, Russia.