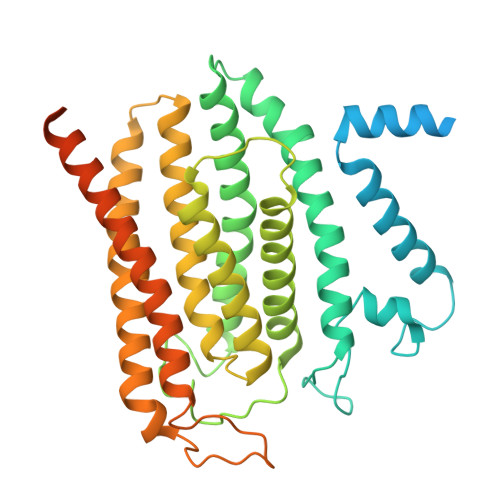
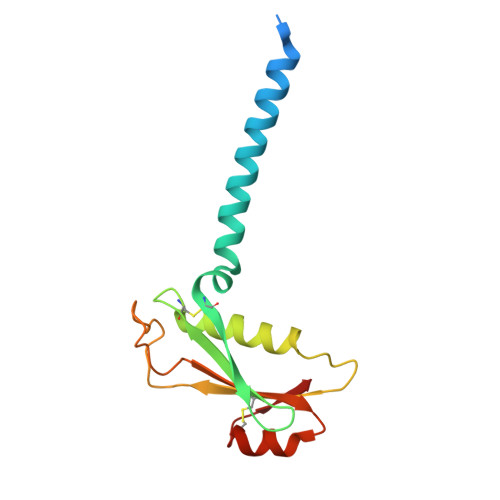
Mechanism of ceramide synthase inhibition by fumonisin B 1.
Zhang, Z., Fang, Q., Xie, T., Gong, X.(2024) Structure 32: 1419-1428.e4
- PubMed: 38964337
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2024.06.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8Y2M, 8Y2N, 8ZB1 - PubMed Abstract:
Ceramide synthases (CerSs) play crucial roles in sphingolipid metabolism and have emerged as promising drug targets for metabolic diseases, cancers, and antifungal therapy. However, the therapeutic targeting of CerSs has been hindered by a limited understanding of their inhibition mechanisms by small molecules. Fumonisin B 1 (FB 1 ) has been extensively studied as a potent inhibitor of eukaryotic CerSs. In this study, we characterize the inhibition mechanism of FB 1 on yeast CerS (yCerS) and determine the structures of both FB 1 -bound and N-acyl-FB 1 -bound yCerS. Through our structural analysis and the observation of N-acylation of FB 1 by yCerS, we propose a potential ping-pong catalytic mechanism for FB 1 N-acylation by yCerS. Lastly, we demonstrate that FB 1 exhibits lower binding affinity for yCerS compared to the C26- coenzyme A (CoA) substrate, suggesting that the potent inhibitory effect of FB 1 on yCerS may primarily result from the N-acyl-FB 1 catalyzed by yCerS, rather than through direct binding of FB 1 .
Organizational Affiliation:
Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Plant Genetic Engineering and Molecular Design, Department of Biology, School of Life Sciences, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518055, China; Department of Chemical Biology, School of Life Sciences, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518055, China.