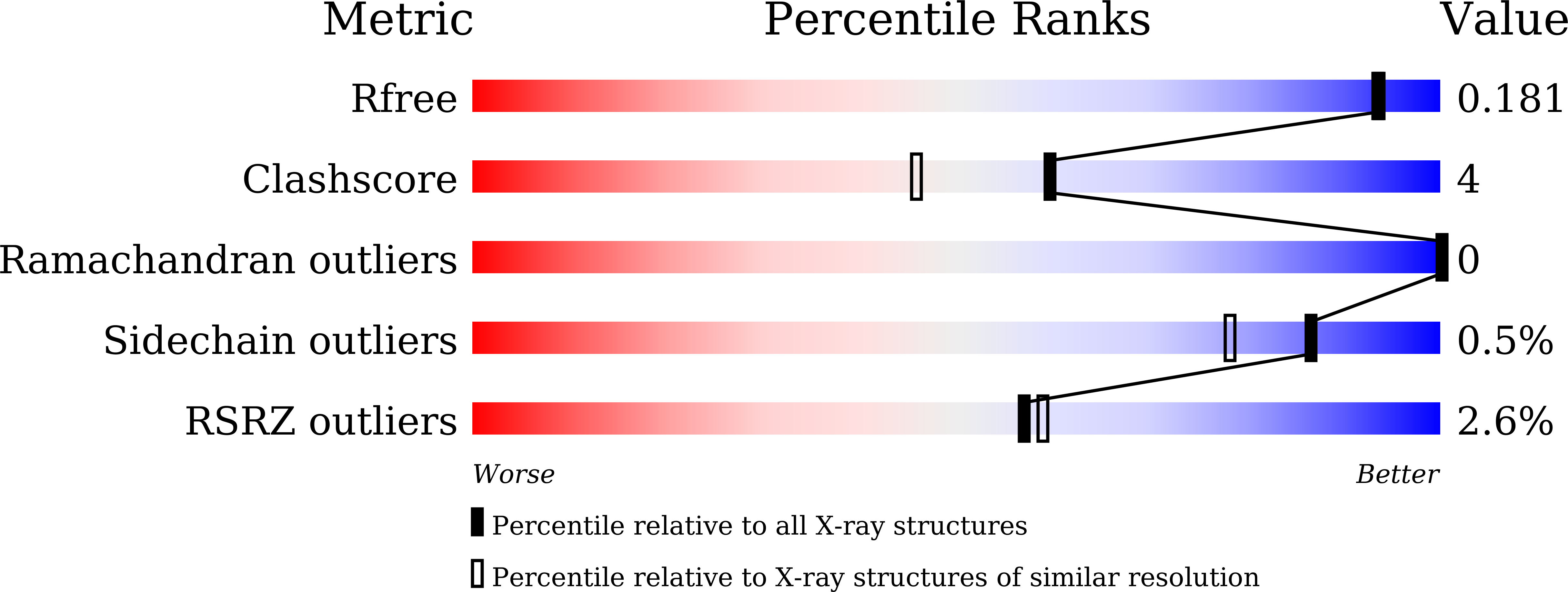
Structural basis for psilocybin biosynthesis.
Meng, C., Guo, W., Xiao, C., Wen, Y., Zhu, X., Zhang, Q., Liang, Y., Li, H., Xu, S., Qiu, Y., Chen, H., Lin, W.J., Wu, B.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 2827-2827
- PubMed: 40121242
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58239-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8X4Q, 8X4S, 8ZIA, 8ZIC, 8ZIE, 8ZIG, 8ZIH, 8ZII, 8ZIM, 8ZIO - PubMed Abstract:
Psilocybin shows significant therapeutic potential for psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy in addressing various psychiatric conditions. The biosynthetic approach promises rapid and efficient production of psilocybin. Understanding the enzymes that contribute to the biosynthesis of psilocybin can enhance its production process. In this study, we elucidate the crystal structures of L-tryptophan-specific decarboxylase PsiD in both its apo and tryptamine-bound states, the 4-hydroxytryptamine kinase PsiK bound to its substrate, and several forms of the methyltransferase PsiM in either apo or substrate-bound forms derived from the psychedelic mushroom. Structure-based evaluations reveal the mechanisms of self-cleavage and self-inhibition in PsiD, along with the sequential catalytic steps from 4-hydroxytryptamine to the final compound, psilocybin. Additionally, we showcase the antidepressant properties of biosynthetic intermediates of psilocybin on female mice experiencing depression-like behaviors induced by sub-chronic variable stress. Our studies establish a structural basis for the future biosynthetic production of psilocybin using these enzymes and emphasize the clinical potential of norbaeocystin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Epigenetics and Gene Regulation, Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory for RNA Medicine, Medical Research Center, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China.