The Structure of the Extracellular Region of Human Hepsin Reveals a Serine Protease Domain and a Novel Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich (SRCR) Domain
Somoza, J.R., Ho, J.D., Luong, C., Ghate, M., Sprengeler, P.A., Mortara, K., Shrader, W.D., Sperandio, D., Chan, H., McGrath, M.E., Katz, B.A.(2003) Structure 11: 1123-1131
- PubMed: 12962630
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(03)00148-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1P57 - PubMed Abstract:
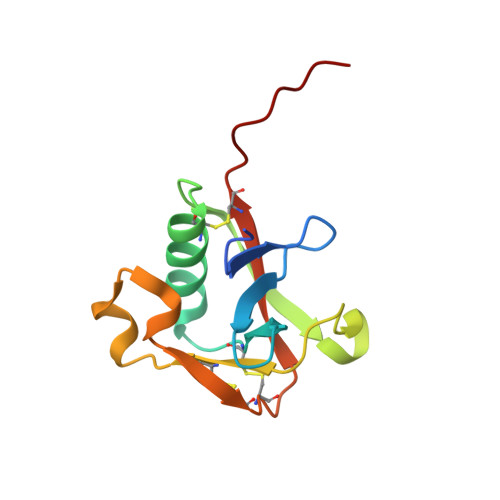
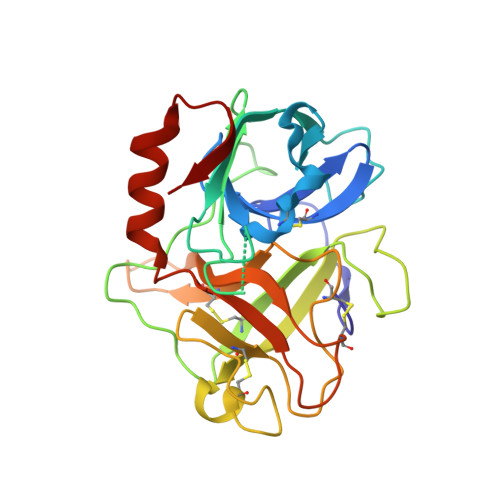
Hepsin is an integral membrane protein that may participate in cell growth and in maintaining proper cell morphology and is overexpressed in a number of primary tumors. We have determined the 1.75 A resolution structure of the extracellular component of human hepsin. This structure includes a 255-residue trypsin-like serine protease domain and a 109-residue region that forms a novel, poorly conserved, scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain. The two domains are associated with each other through a single disulfide bond and an extensive network of noncovalent interactions. The structure suggests how the extracellular region of hepsin may be positioned with respect to the plasma membrane.
Organizational Affiliation:
Celera, Inc., 180 Kimball Road, South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA. john.somoza@celera.com