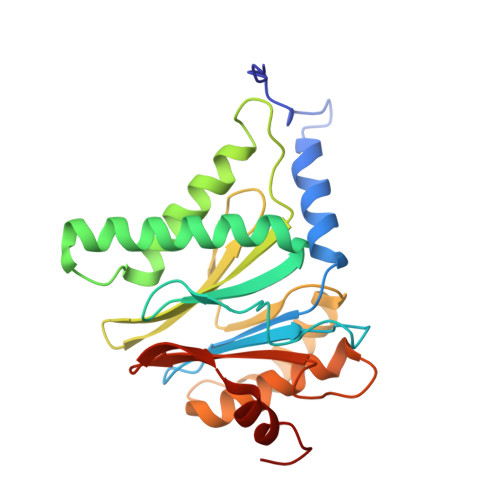
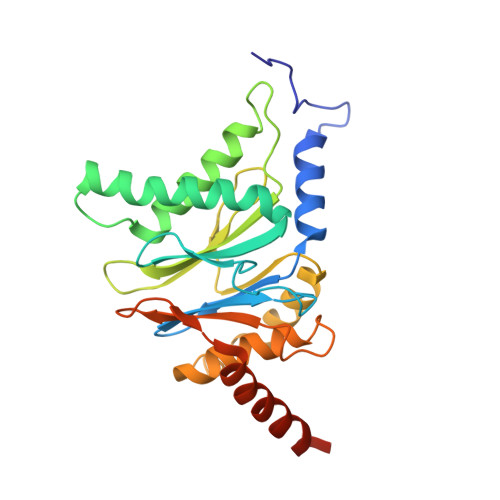
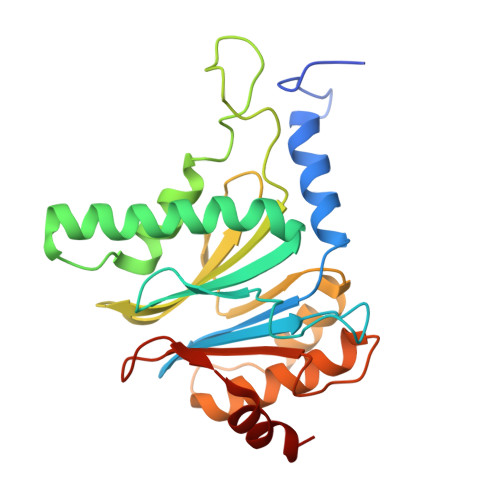
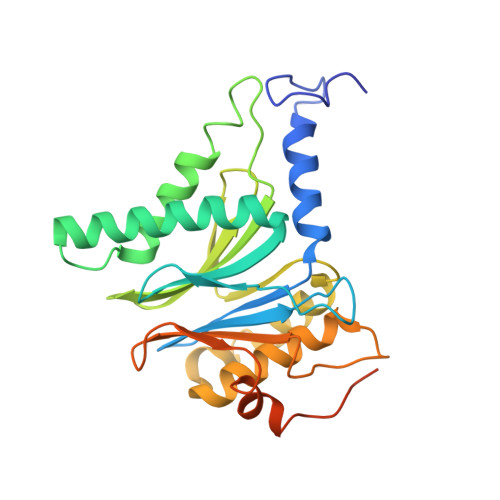
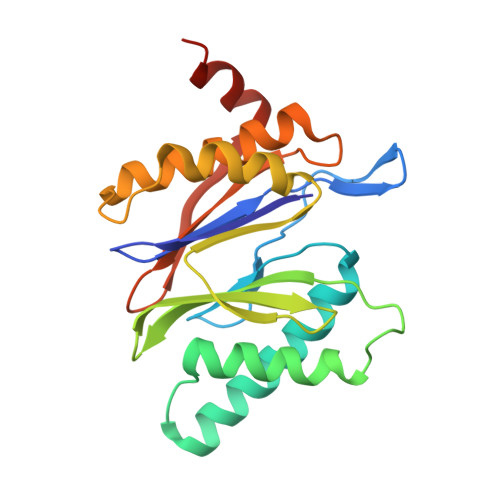
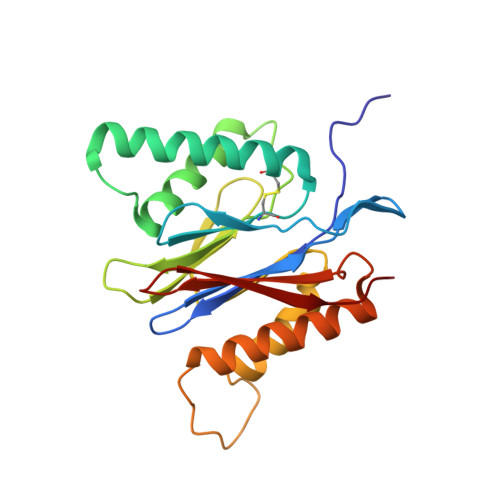
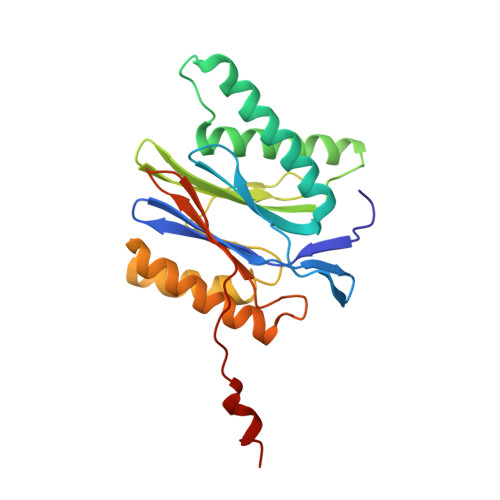
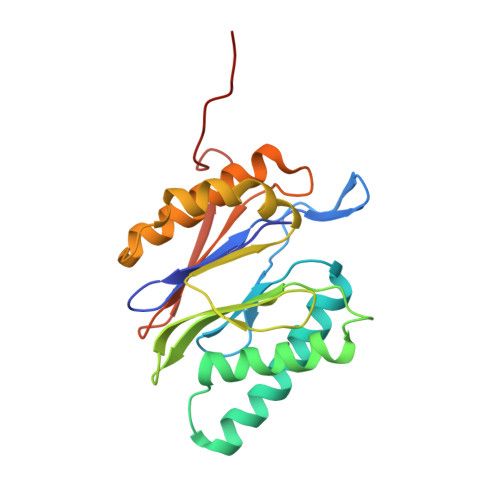
Immuno- and constitutive proteasome crystal structures reveal differences in substrate and inhibitor specificity.
Huber, E.M., Basler, M., Schwab, R., Heinemeyer, W., Kirk, C.J., Groettrup, M., Groll, M.(2012) Cell 148: 727-738
- PubMed: 22341445
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.030
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3UN4, 3UN8, 3UNB, 3UNE, 3UNF, 3UNH - PubMed Abstract:
Constitutive proteasomes and immunoproteasomes shape the peptide repertoire presented by major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules by harboring different sets of catalytically active subunits. Here, we present the crystal structures of constitutive proteasomes and immunoproteasomes from mouse in the presence and absence of the epoxyketone inhibitor PR-957 (ONX 0914) at 2.9 ? resolution. Based on our X-ray data, we propose a unique catalytic feature for the immunoproteasome subunit ¦Â5i/LMP7. Comparison of ligand-free and ligand-bound proteasomes reveals conformational changes in the S1 pocket of ¦Â5c/X but not ¦Â5i, thereby explaining the selectivity of PR-957 for ¦Â5i. Time-resolved structures of yeast proteasome:PR-957 complexes indicate that ligand docking to the active site occurs only via the reactive head group and the P1 side chain. Together, our results support structure-guided design of inhibitory lead structures selective for immunoproteasomes that are linked to cytokine production and diseases like cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Integrated Protein Science at the Department Chemie, Lehrstuhl f¨¹r Biochemie, Technische Universit?t M¨¹nchen, Garching D-85747, Germany.