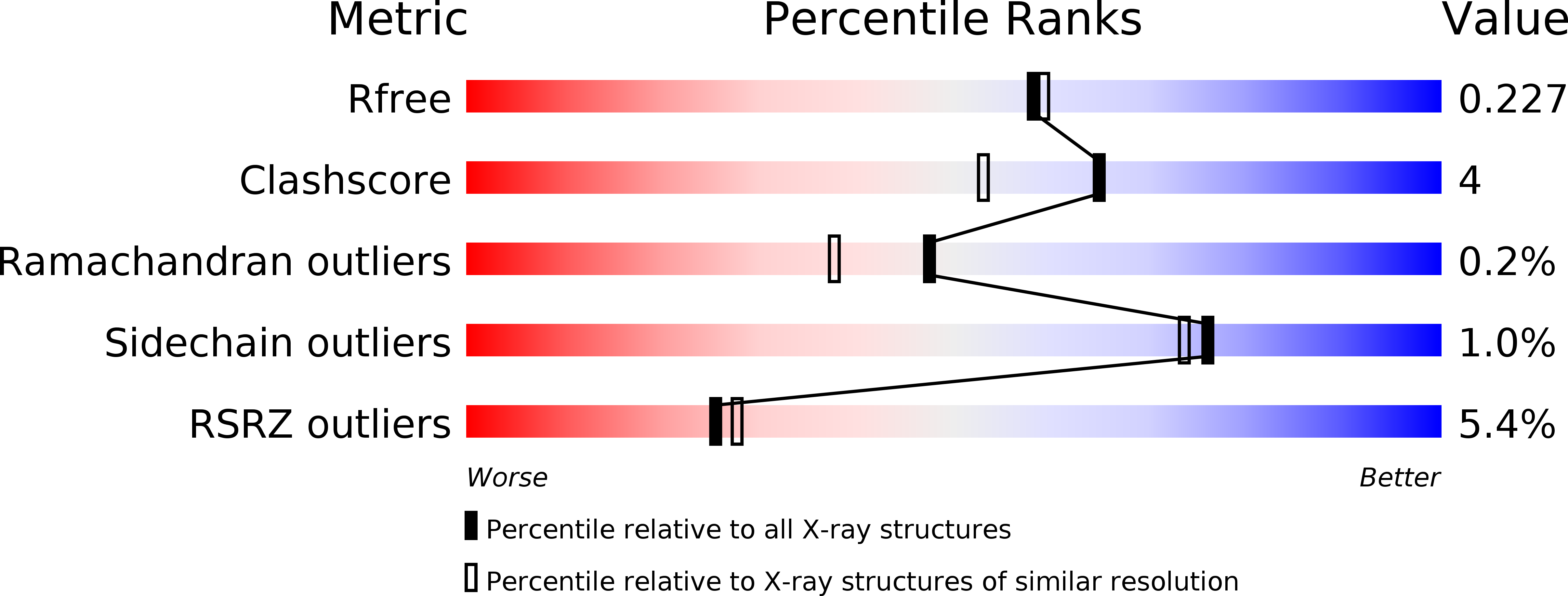
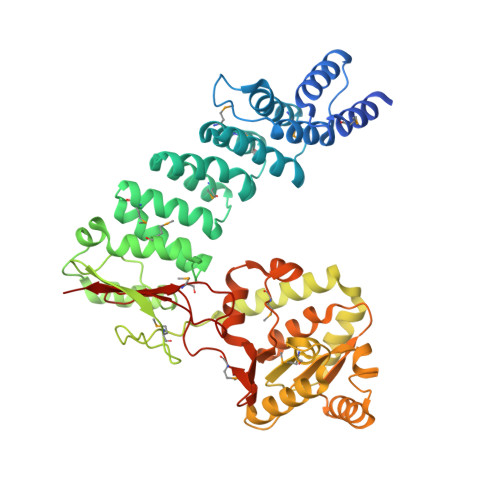
Mitochondrial ribonuclease P structure provides insight into the evolution of catalytic strategies for precursor-tRNA 5' processing.
Howard, M.J., Lim, W.H., Fierke, C.A., Koutmos, M.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 16149-16154
- PubMed: 22991464
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209062109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4G23, 4G24, 4G25, 4G26 - PubMed Abstract:
Ribonuclease P (RNase P) catalyzes the maturation of the 5' end of tRNA precursors. Typically these enzymes are ribonucleoproteins with a conserved RNA component responsible for catalysis. However, protein-only RNase P (PRORP) enzymes process precursor tRNAs in human mitochondria and in all tRNA-using compartments of Arabidopsis thaliana. PRORP enzymes are nuclear encoded and conserved among many eukaryotes, having evolved recently as yeast mitochondrial genomes encode an RNase P RNA. Here we report the crystal structure of PRORP1 from A. thaliana at 1.75 ? resolution, revealing a prototypical metallonuclease domain tethered to a pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) domain by a structural zinc-binding domain. The metallonuclease domain is a unique high-resolution structure of a Nedd4-BP1, YacP Nucleases (NYN) domain that is a member of the PIN domain-like fold superfamily, including the FLAP nuclease family. The structural similarity between PRORP1 and the FLAP nuclease family suggests that they evolved from a common ancestor. Biochemical data reveal that conserved aspartate residues in PRORP1 are important for catalytic activity and metal binding and that the PPR domain also enhances activity, likely through an interaction with pre-tRNA. These results provide a foundation for understanding tRNA maturation in organelles. Furthermore, these studies allow for a molecular-level comparison of the catalytic strategies used by the only known naturally evolved protein and RNA-based catalysts that perform the same biological function, pre-tRNA maturation, thereby providing insight into the differences between the prebiotic RNA world and the present protein-dominated world.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA.