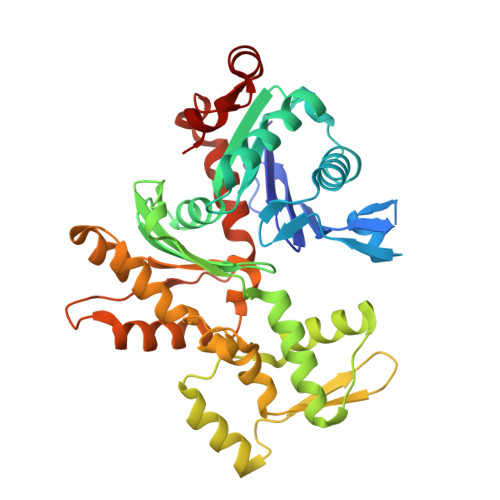
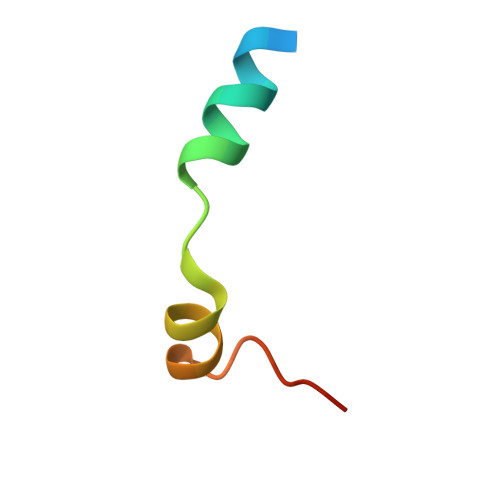
Structures of the Phactr1 RPEL domain and RPEL motif complexes with G-actin reveal the molecular basis for actin binding cooperativity.
Mouilleron, S., Wiezlak, M., O'Reilly, N., Treisman, R., McDonald, N.Q.(2012) Structure 20: 1960-1970
- PubMed: 23041370
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.08.031
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4B1U, 4B1V, 4B1W, 4B1X, 4B1Y, 4B1Z - PubMed Abstract:
The Phactr family of PP1-binding proteins and the myocardin-related transcription factor family of transcriptional coactivators contain regulatory domains comprising three copies of the RPEL motif, a G-actin binding element. We report the structure of a Phactr1 G-actin?RPEL domain complex. Three G-actins surround the crank-shaped RPEL domain forming?a closed helical assembly. Their spatial relationship is identical to the RPEL-actins within the pentavalent MRTF G-actin?RPEL domain complex, suggesting that conserved cooperative interactions between actin?RPEL units organize the assembly. In the trivalent Phactr1 complex, each G-actin?RPEL unit makes secondary contacts with its downstream actin involving distinct RPEL residues. Similar secondary contacts are seen in G-actin?RPEL peptide crystals. Loss-of-secondary-contact mutations destabilize the Phactr1 G-actin?RPEL assembly. Furthermore, actin-mediated inhibition of Phactr1 nuclear import requires secondary contact residues in the Phactr1 N-terminal RPEL-N motif, suggesting that it involves interaction of RPEL-N with the C-terminal assembly. Secondary actin contacts by actin-bound RPEL motifs thus govern formation of multivalent actin?RPEL assemblies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology, CRUK London Research Institute, 44 Lincoln's Inn Fields, London WC2A 3LY, UK.