Six independent fucose-binding sites in the crystal structure of Aspergillus oryzae lectin
Makyio, H., Shimabukuro, J., Suzuki, T., Imamura, A., Ishida, H., Kiso, M., Ando, H., Kato, R.(2016) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477: 477-482
- PubMed: 27318092
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.069
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5EO7, 5EO8 - PubMed Abstract:
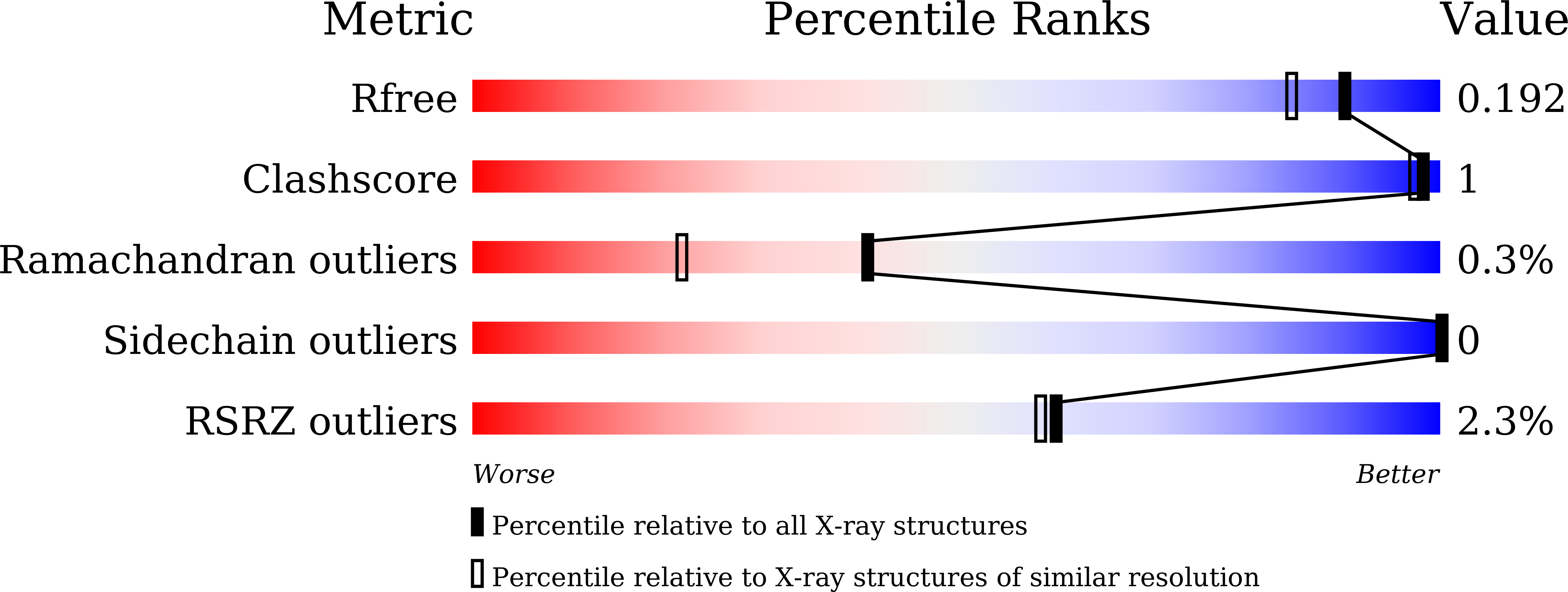
The crystal structure of AOL (a fucose-specific lectin of Aspergillus oryzae) has been solved by SAD (single-wavelength anomalous diffraction) and MAD (multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction) phasing of seleno-fucosides. The overall structure is a six-bladed ¦Â-propeller similar to that of other fucose-specific lectins. The fucose moieties of the seleno-fucosides are located in six fucose-binding sites. Although the Arg and Glu/Gln residues bound to the fucose moiety are common to all fucose-binding sites, the amino-acid residues involved in fucose binding at each site are not identical. The varying peak heights of the seleniums in the electron density map suggest that each fucose-binding site has a different carbohydrate binding affinity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Research Center, Photon Factory, Institute of Materials Structure Science, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK), 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-0801, Japan.