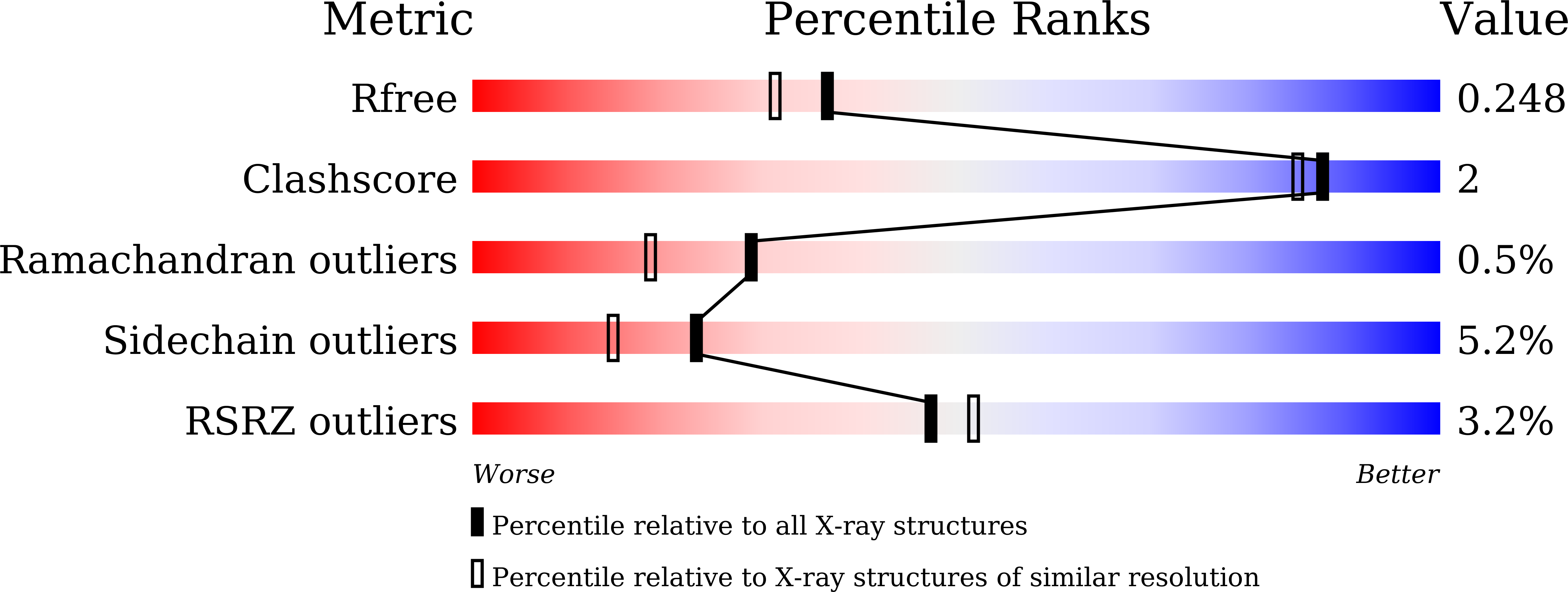
Crystal Structure and Potential Head-to-Middle Condensation Function of aZ,Z-Farnesyl Diphosphate Synthase.
Chan, Y.T., Ko, T.P., Yao, S.H., Chen, Y.W., Lee, C.C., Wang, A.H.(2017) ACS Omega 2: 930-936
- PubMed: 30023621
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.6b00562
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5HXN, 5HXO, 5HXP - PubMed Abstract:
Plants produce a wide variety of secondary metabolites in response to adverse environmental factors. Z , Z -Farnesyl diphosphate ( Z , Z -FPP), synthesized by Z , Z -farnesyl diphosphate synthase ( z FPS), supports the formation of phytochemicals in wild tomatoes. Here, the crystal structure of N-terminal truncated z FPS (¦¤ z FPS) was determined. Irregular products including lavandulyl diphosphate and an unknown compound were surprisingly found. Apart from the truncated N-terminus as a functional regulator, structure-based analysis and mutagenesis assays revealed a residue H103 in ¦¤ z FPS as one of the key elements to this irregular function. A series of substrate-enzyme complex structures were obtained from ¦¤ z FPS-H103Y by co-crystallizing with isopentenyl diphosphate, dimethylallyl thiolodiphosphate, or both. Various substrate-binding modes were revealed. The catalytic mechanisms of both the head-to-tail and head-to-middle reactions in ¦¤ z FPS were proposed. Functional switch between the two mechanisms in this enzyme and the essential role played by the flexible C-terminus were elucidated as well.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica, Taipei 115, Taiwan.