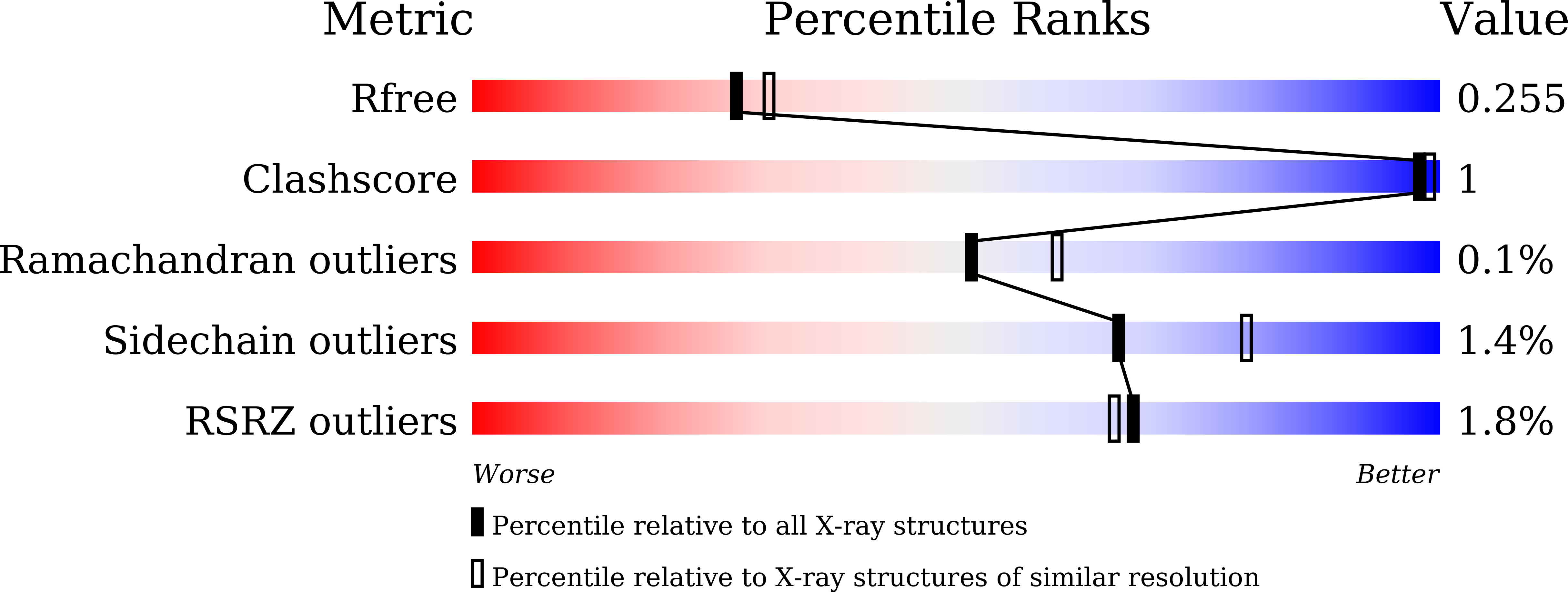
Direct Hydroxylation of Benzene to Phenol by Cytochrome P450BM3 Triggered by Amino Acid Derivatives.
Shoji, O., Yanagisawa, S., Stanfield, J.K., Suzuki, K., Cong, Z., Sugimoto, H., Shiro, Y., Watanabe, Y.(2017) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56: 10324-10329
- PubMed: 28544674
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201703461
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XA3 - PubMed Abstract:
The selective hydroxylation of benzene to phenol, without the formation of side products resulting from overoxidation, is catalyzed by cytochrome P450BM3 with the assistance of amino acid derivatives as decoy molecules. The catalytic turnover rate and the total turnover number reached 259?min -1 ?P450BM3 -1 and 40?200?P450BM3 -1 when N-heptyl-l-proline modified with l-phenylalanine (C7-l-Pro-l-Phe) was used as the decoy molecule. This work shows that amino acid derivatives with a totally different structure from fatty acids can be used as decoy molecules for aromatic hydroxylation by wild-type P450BM3. This method for non-native substrate hydroxylation by wild-type P450BM3 has the potential to expand the utility of P450BM3 for biotransformations.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, Furo-cho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, 464-8602, Japan.