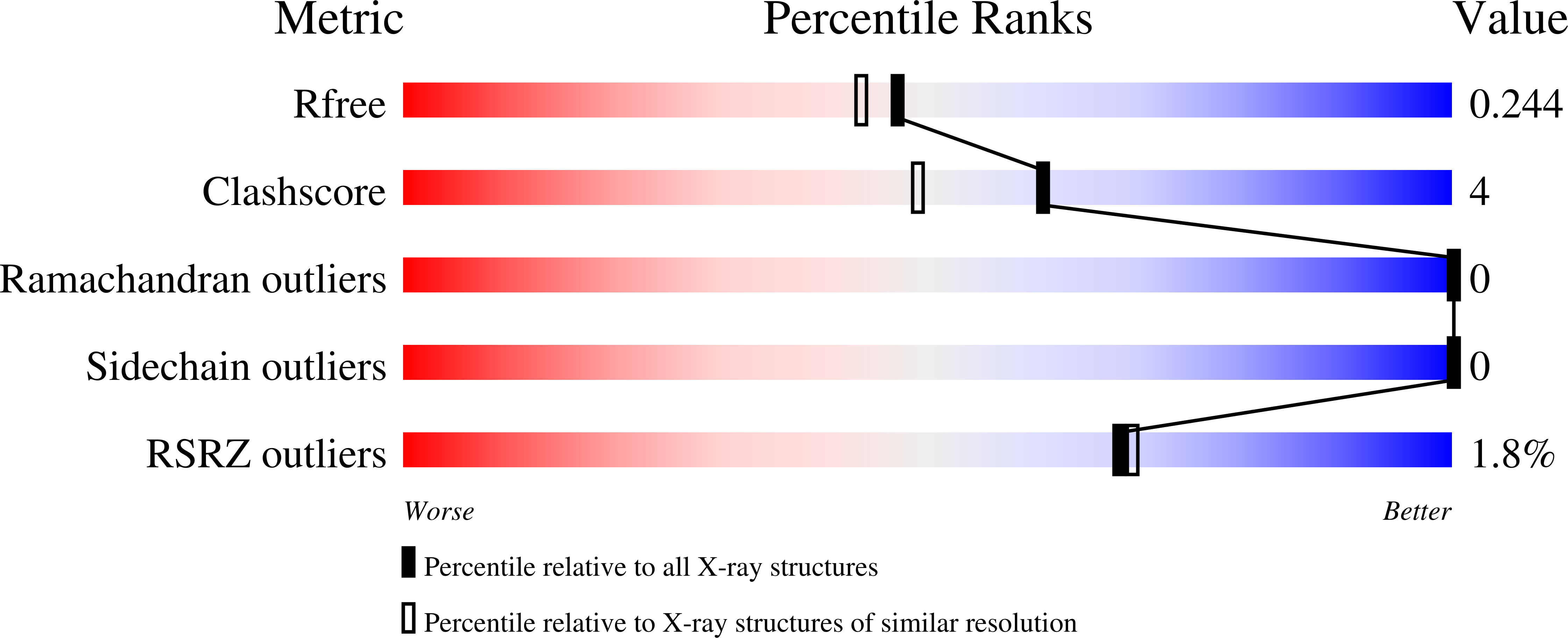
Structural basis for selective inhibition of human PKG I alpha by the balanol-like compound N46.
Qin, L., Sankaran, B., Aminzai, S., Casteel, D.E., Kim, C.(2018) J Biological Chem 293: 10985-10992
- PubMed: 29769318
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002427
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6C0T, 6C0U - PubMed Abstract:
Activation of protein kinase G (PKG) I¦Á in nociceptive neurons induces long-term hyperexcitability that causes chronic pain. Recently, a derivative of the fungal metabolite balanol, N46, has been reported to inhibit PKG I¦Á with high potency and selectivity and attenuate thermal hyperalgesia and osteoarthritic pain. Here we determined co-crystal structures of the PKG I¦Á C-domain and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) C¦Á, each bound with N46, at 1.98 ? and 2.65 ?, respectively. N46 binds the active site with its external phenyl ring, specifically interacting with the glycine-rich loop and the ¦ÁC helix. Phe-371 at the PKG I¦Á glycine-rich loop is oriented parallel to the phenyl ring of N46, forming a strong ¦Ð-stacking interaction, whereas the analogous Phe-54 in PKA C¦Á rotates 30¡ã and forms a weaker interaction. Structural comparison revealed that steric hindrance between the preceding Ser-53 and the propoxy group of the phenyl ring may explain the weaker interaction with PKA C¦Á. The analogous Gly-370 in PKG I¦Á, however, causes little steric hindrance with Phe-371. Moreover, Ile-406 on the ¦ÁC helix forms a hydrophobic interaction with N46 whereas its counterpart in PKA, Thr-88, does not. Substituting these residues in PKG I¦Á with those in PKA C¦Á increases the IC 50 values for N46, whereas replacing these residues in PKA C¦Á with those in PKG I¦Á reduces the IC 50 , consistent with our structural findings. In conclusion, our results explain the structural basis for N46-mediated selective inhibition of human PKG I¦Á and provide a starting point for structure-guided design of selective PKG I¦Á inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas 77030.