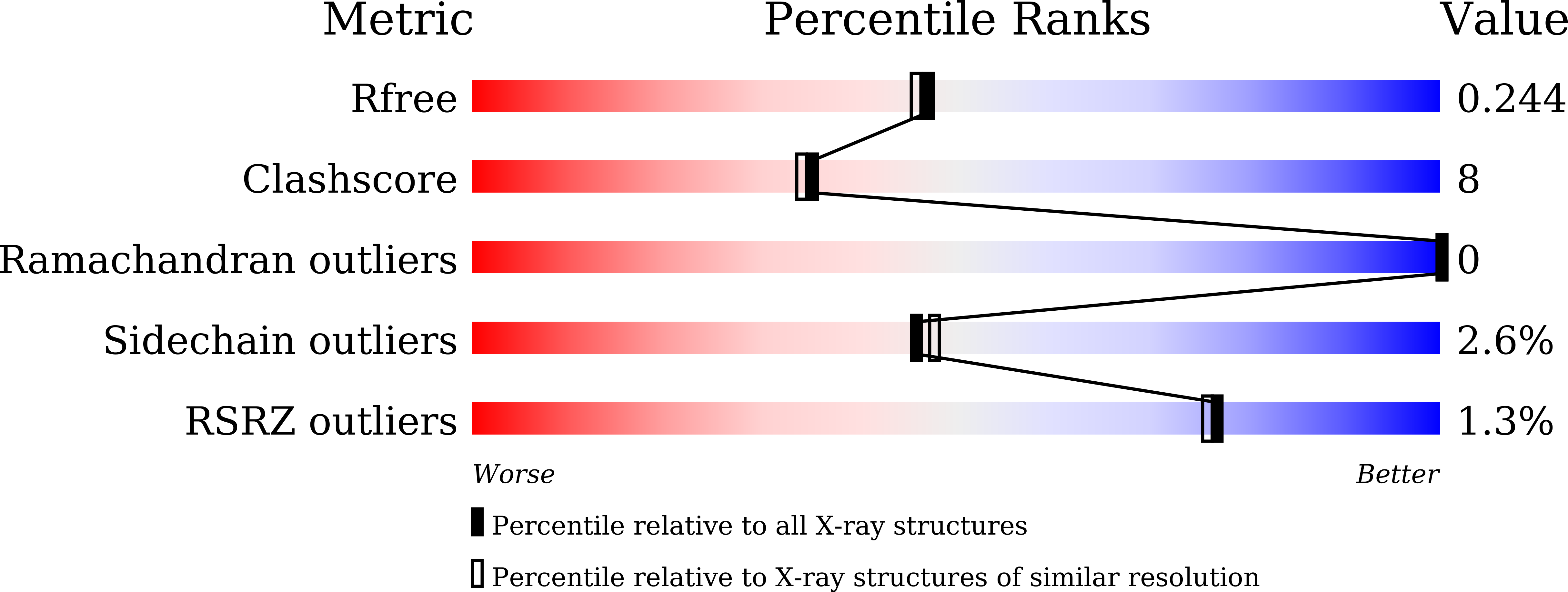
Engineering of two thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzymes for the regioselective condensation of C1-formaldehyde into C4-erythrulose.
Kim, J.H., Cheon, H., Jo, H.J., Kim, J.W., Kim, G.Y., Seo, H.R., Seo, P.W., Kim, J.S., Park, J.B.(2023) Int J Biol Macromol 253: 127674-127674
- PubMed: 37890751
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127674
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8I01, 8I05, 8I07, 8I08 - PubMed Abstract:
A number of carboligases, which catalyze condensation of C1- and/or C2-aldehydes into multi-carbon products, have been reported. However, their catalytic activities and/or regioselectivities remained rather low. Thereby, this study has focused on engineering of C1 and C2 carboligases for the regioselective condensation of C1-formaldehyde into C4-erythrulose via C2-glycolaldehyde. The crystal structure of the glyoxylate carboligase from Escherichia coli (EcGCL) was elucidated in complex with glycolaldehyde. A structure-guided rationale generated several mutants, one of whose catalytic activity reached 15.6?M -1 ¡¤s -1 , almost 10 times greater than the wild-type enzyme. Another variant (i.e., EcGCL _R484M/N283Q/L478M/M488L/R284K ) has shown significantly increased stability to the glycolaldehyde toxicity, enabling production of glycolaldehyde to 31?mM from 75?mM formaldehyde (conversion: 83?%). Besides, the E1 subunit of ¦Á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex from Vibrio vulnificus (VvSucA) was engineered as a regiospecific C2 carboligase for condensation of glycolaldehyde into erythrulose. The combination of EcGCL _R484M/N283Q/L478M/M488L/R284K and VvSucA _K228L led to the cascade production of erythrulose to 8?mM from 90?mM formaldehyde via glycolaldehyde without byproduct formation. This study will contribute to valorization of C1 gases into industrially relevant multi-carbon products in an environment-friendly way.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Republic of Korea.