Artificial Metalloenzymes with Two Catalytic Cofactors for Tandem Abiotic Transformations.
Wang, W., Tachibana, R., Zhang, K., Lau, K., Pojer, F., Ward, T.R., Hu, X.(2025) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl : e202422783-e202422783
- PubMed: 39760306
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202422783
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
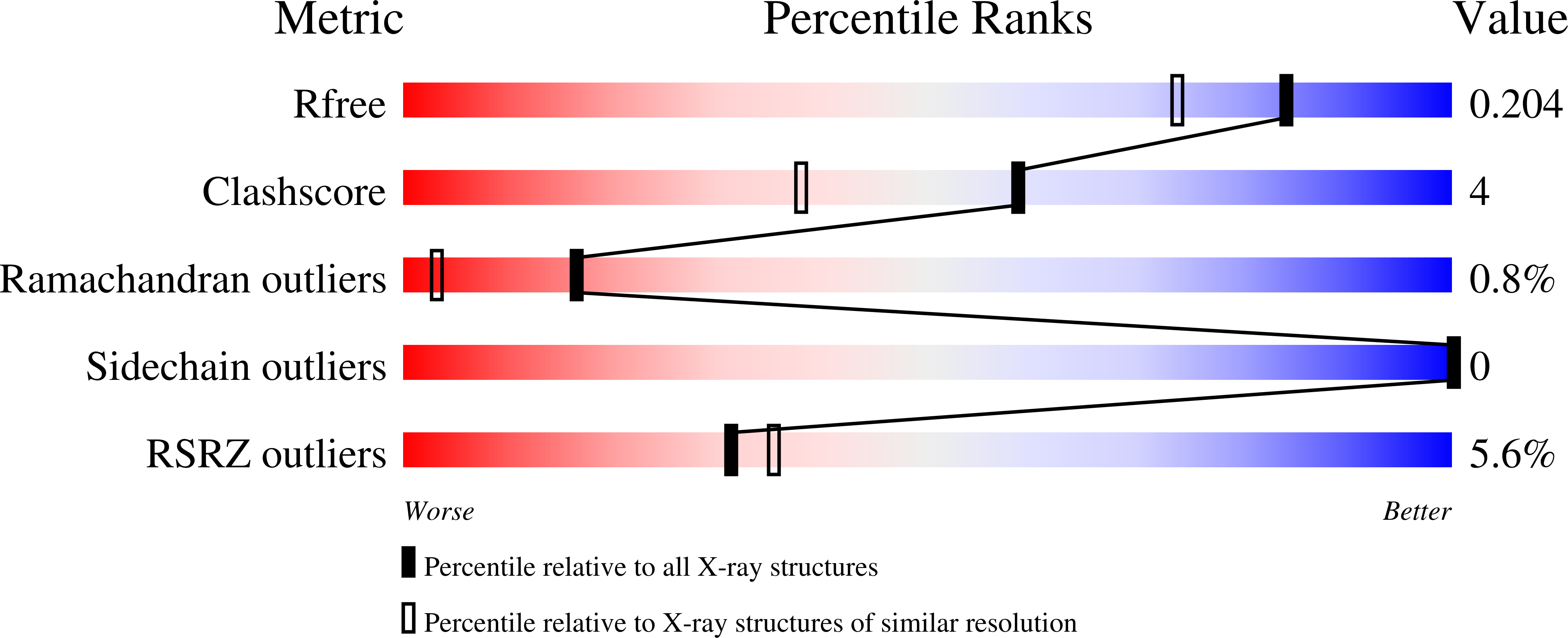
9FFJ, 9FNR, 9FOA - PubMed Abstract:
Artificial metalloenzymes (ArMs) enable the integration of abiotic cofactors within a native protein scaffold, allowing for non-natural catalytic activities. Previous ArMs, however, have primarily relied on single cofactor systems, limiting them to only one catalytic function. Here we present an approach to construct ArMs embedding two catalytic cofactors based on the biotin-streptavidin technology. By incorporating multiple catalytic cofactors into the four binding sites of streptavidin, we engineered programmable ArMs for tandem abiotic transformations including an enantioselective formal C-H hydroxylation and a photooxidation-Michael addition. This work thus outlines a promising strategy for the development of ArMs embedding multiple cofactors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Catalysis, Institute of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, ?cole Polytechnique F¨¦d¨¦rale de Lausanne, I, SIC-LSCI, BCH 3305, Lausanne, 1015, Switzerland Website.