Highly Optimized CNS Penetrant Inhibitors of EGFR Exon20 Insertion Mutations.
McCoull, W., Thomson, C., Braybrooke, E., Chan, C., Colclough, N., Cortes Gonzalez, M.A., Cosulich, S., Davies, N.L., Floc'h, N., Greenwood, R., Hargreaves, D., Huang, P., Hunt, T.A., Johnson, T., Johnstrom, P., Kettle, J.G., Kondrashov, M., Kostomiris, D.H., Li, S., Lister, A., Martin, S., McKerrecher, D., McLean, N., Nissink, J.W.M., Orme, J.P., Orwig, P., Packer, M.J., Pearson, S., Qin, L., Felisberto-Rodrigues, C., Savoca, A., Schou, M., Stokes, S., Swaih, A.M., Talbot, S., Tucker, M.J., Ward, R.A., Wadforth, E., Wang, C., Wilson, J., Yang, Y.(2025) J Med Chem
- PubMed: 39869768
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02811
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
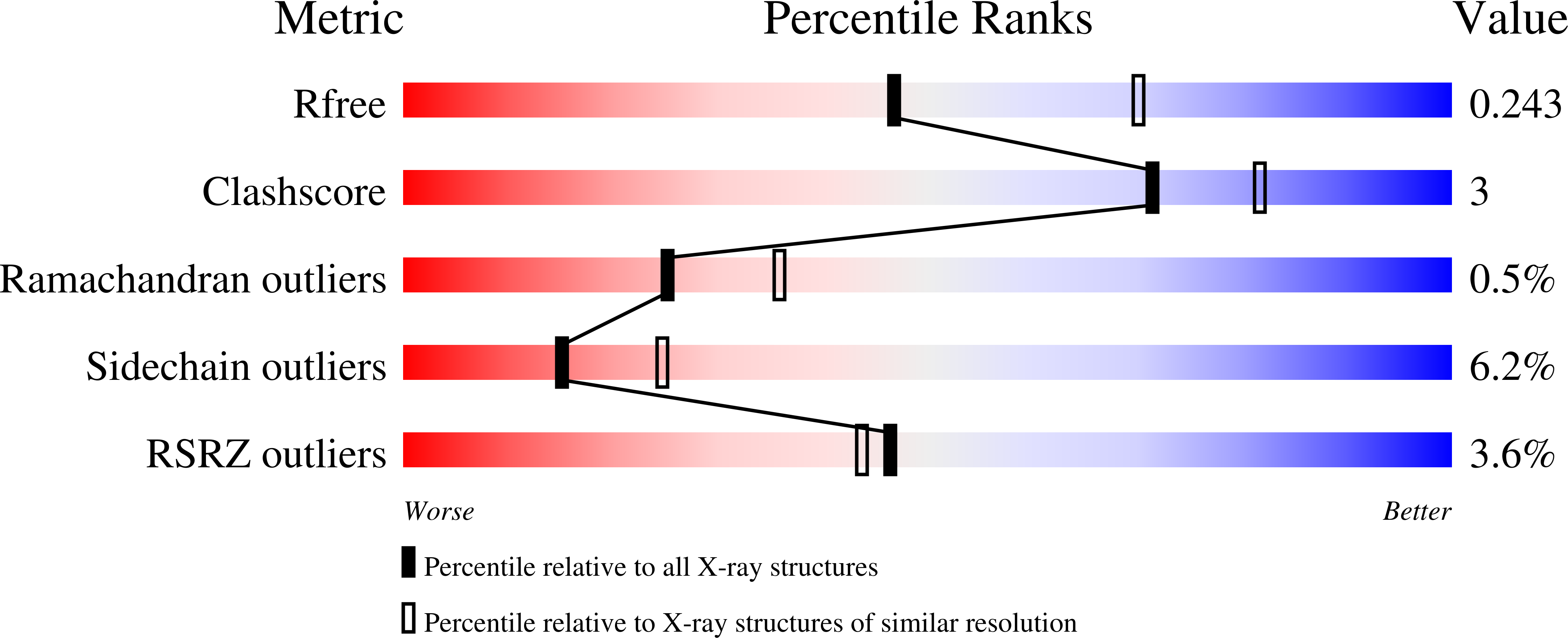
9GC4, 9GC5, 9GC6, 9GDV, 9HBO - PubMed Abstract:
Despite recent advances in the inhibition of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor), there remains a clinical need for new EGFR Exon20 insertion (Ex20Ins) inhibitors that spare EGFR WT. Herein, we report the discovery and optimization of two chemical series leading to ether 23 and biaryl 36 as potent, selective, and brain-penetrant inhibitors of Ex20Ins mutants. Building on our earlier discovery of alkyne 5 which allowed access to CNS property space for an Ex20Ins inhibitor, we utilized structure-based design to move to lower lipophilicity and lower CL int compounds while maintaining a WT selectivity margin. During optimization, aldehyde oxidase (AO) metabolism was identified as a human clearance risk, and through SAR exploration, lower AO metabolism was achieved. Potency and WT margin were optimized across a range of Ex20Ins mutants including the potential acquired resistance T790M mutant and efficacy demonstrated in an LXF2478 Ex20Ins ASV model with margin to EGFR WT in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
AstraZeneca, 1 Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Cambridge CB2 0AA, U.K.