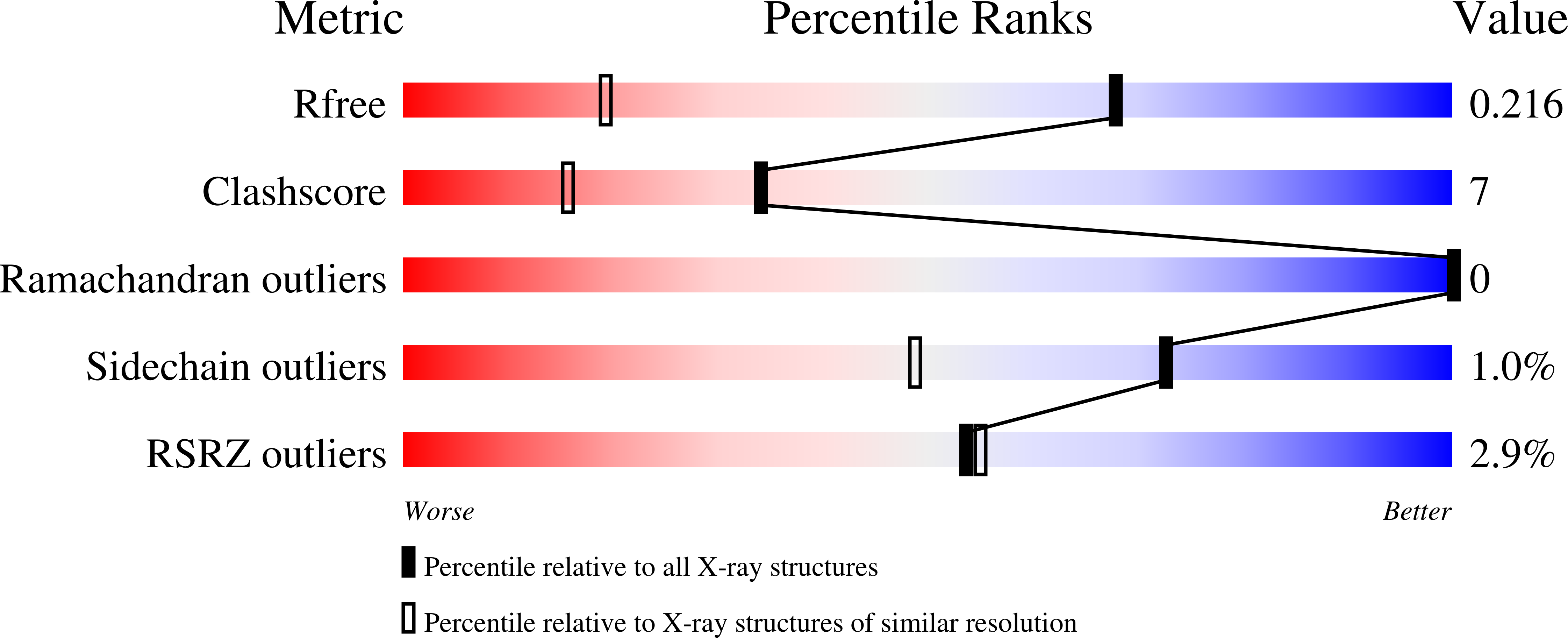
Kinetic and structural investigation of the 4-allyl syringol oxidase from Streptomyces cavernae.
Eggerichs, D., Weddeling, H.G., Alvigini, L., Rapsch, T., Weindorf, N., Mattevi, A., Tischler, D.(2025) Arch Biochem Biophys 765: 110320-110320
- PubMed: 39870290
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2025.110320
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9GOV, 9GOZ, 9GP0 - PubMed Abstract:
4-Phenol oxidases are proposed to be involved in the utilization of lignin-derived aromatic compounds. While enzymes with selectivity towards 4-hydroxyphenyl and guaiacyl motifs are well described, we identified the first syringyl-specific oxidase from Streptomyces cavernae (Sc4ASO) only very recently. Here, in-depth studies were conducted to unravel the molecular origins of the outstanding selectivity of Sc4ASO. Kinetic experiments revealed high activities on dimethoxylated substrates (up to 2.9?¡À?0.1 s -1 ), but also strong cooperativity between both protein subunits, as well as substrate inhibition in dependency of ortho methoxylation and chain length of the para substituent. Rapid mixing kinetics in combination with the determination of the crystal structure in complex with three substrates allowed to connect the kinetic behavior with never-observed positioning of the conserved residue Y471. Ultimately, the catalytic potential of Sc4ASO was investigated in a 100?mL scale cascade reaction to produce the natural product syringaresinol.
Organizational Affiliation:
Microbial Biotechnology, Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology, Ruhr University Bochum, Universitaetsstrasse 150, 44780, Bochum, Germany.