N-Terminal Protein Binding and Disorder-to-Order Transition by a Synthetic Receptor.
Mockler, N.M., Ramberg, K.O., Flood, R.J., Crowley, P.B.(2025) Biochemistry
- PubMed: 39977527
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00729
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
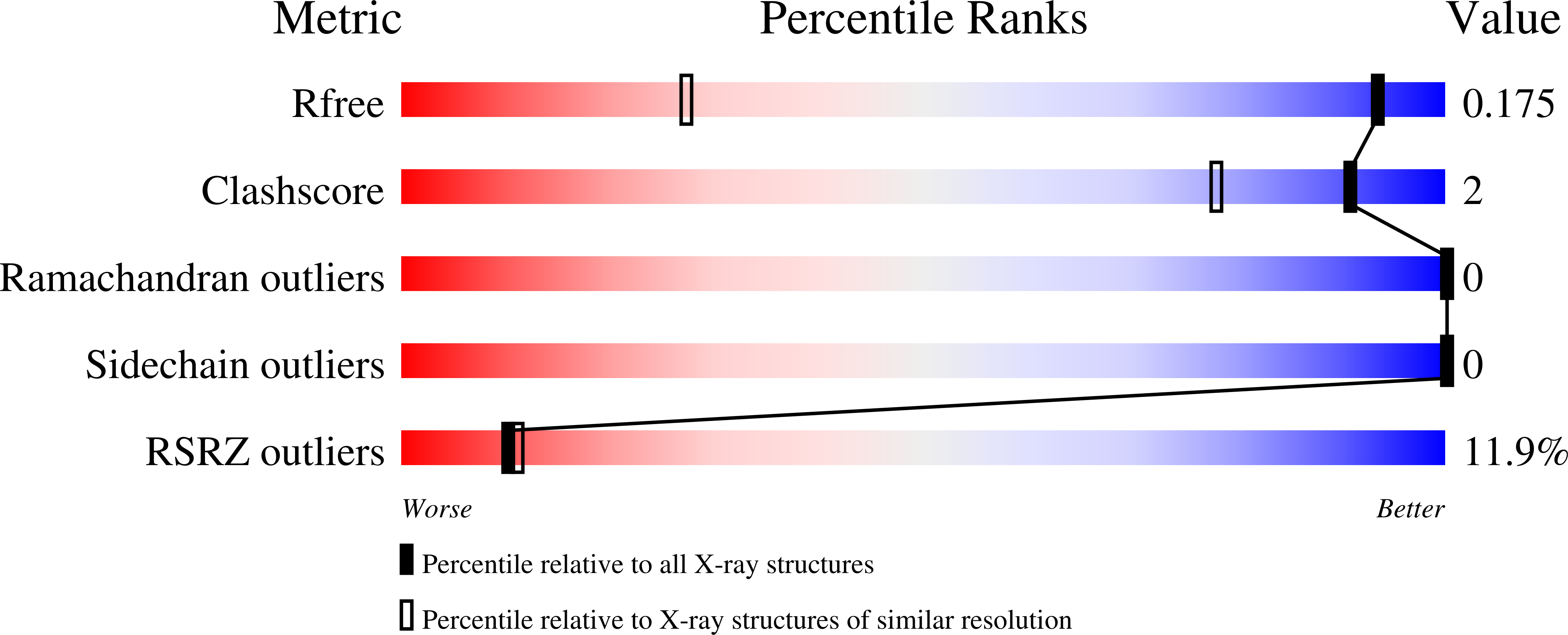
9GR3, 9GR4, 9GR5 - PubMed Abstract:
We describe the capture and structuring of disordered N-terminal regions by the macrocycle sulfonato-calix[4]arene ( sclx 4 ). Using the trimeric ¦Â-propeller Ralstonia solanacearum lectin (RSL) as a scaffold, we generated a series of mutants with extended and dynamic N-termini. Three of the mutants feature an N-terminal methionine-lysine motif. The fourth mutant contains the disordered 8-residue N-terminus of Histone 3, a component of the nucleosome. X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy provide evidence for sclx 4 binding to the flexible N-terminal regions. Three crystal structures reveal that the calixarene recognizes the N-terminal Met-Lys motif, capturing either residue. We provide crystallographic proof for sclx 4 encapsulation of N-terminal methionine. Calixarene capture of intrinsically disordered regions may have applications in regulating protein secondary (and tertiary) structure.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological and Chemical Sciences, University of Galway, Galway H91 TK33, Ireland.