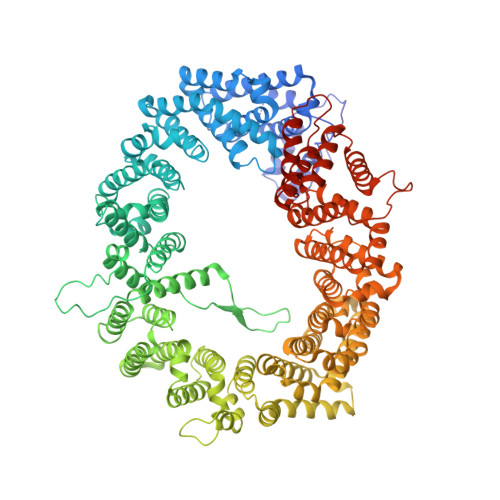
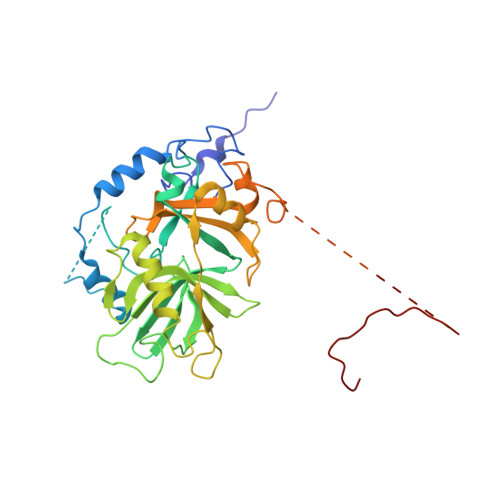
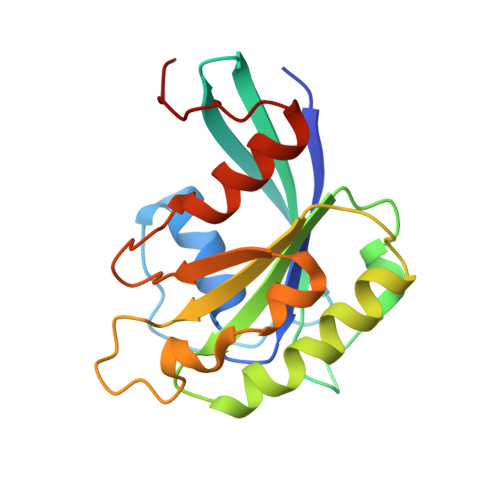
NES consensus redefined by structures of PKI-type and Rev-type nuclear export signals bound to CRM1.
Guttler, T., Madl, T., Neumann, P., Deichsel, D., Corsini, L., Monecke, T., Ficner, R., Sattler, M., Gorlich, D.(2010) Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 1367-1376
- PubMed: 20972448
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1931
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2L1L, 3NBY, 3NBZ, 3NC0, 3NC1 - PubMed Abstract:
Classic nuclear export signals (NESs) confer CRM1-dependent nuclear export. Here we present crystal structures of the RanGTP-CRM1 complex alone and bound to the prototypic PKI or HIV-1 Rev NESs. These NESs differ markedly in the spacing of their key hydrophobic (¦µ) residues, yet CRM1 recognizes them with the same rigid set of five ¦µ pockets. The different ¦µ spacings are compensated for by different conformations of the bound NESs: in the case of PKI, an ¦Á-helical conformation, and in the case of Rev, an extended conformation with a critical proline docking into a ¦µ pocket. NMR analyses of CRM1-bound and CRM1-free PKI NES suggest that CRM1 selects NES conformers that pre-exist in solution. Our data lead to a new structure-based NES consensus, and explain why NESs differ in their affinities for CRM1 and why supraphysiological NESs bind the exportin so tightly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institut f¨ąr Biophysikalische Chemie, G?ttingen, Germany.