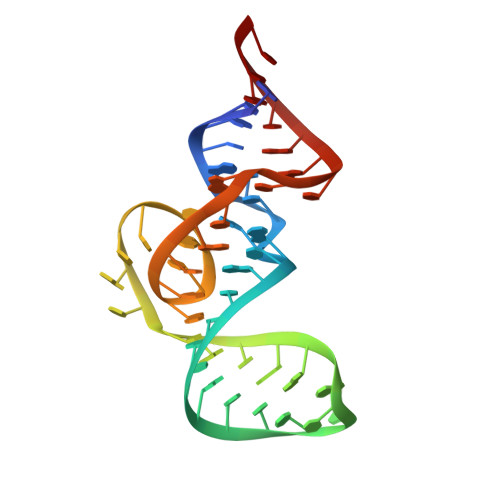
Structure-based investigation of fluorogenic Pepper aptamer.
Huang, K., Chen, X., Li, C., Song, Q., Li, H., Zhu, L., Yang, Y., Ren, A.(2021) Nat Chem Biol 17: 1289-1295
- PubMed: 34725509
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-021-00884-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7EOG, 7EOH, 7EOI, 7EOJ, 7EOK, 7EOL, 7EOM, 7EON, 7EOO, 7EOP - PubMed Abstract:
Pepper fluorescent RNAs are a recently reported bright, stable and multicolor fluorogenic aptamer tag that enable imaging of diverse RNAs in live cells. To investigate the molecular basis of the superior properties of Pepper, we determined the structures of complexes of Pepper aptamer bound with its cognate HBC or HBC-like fluorophores at high resolution by X-ray crystallography. The Pepper aptamer folds in a monomeric non-G-quadruplex tuning-fork-like architecture composed of a helix and one protruded junction region. The near-planar fluorophore molecule intercalates in the middle of the structure and is sandwiched between one non-G-quadruplex base quadruple and one noncanonical G¡¤U wobble helical base pair. In addition, structure-based mutational analysis is evaluated by in vitro and live-cell fluorogenic detection. Taken together, our research provides a structural basis for demystifying the fluorescence activation mechanism of Pepper aptamer and for further improvement of its future application in RNA visualization.
Organizational Affiliation:
Life Sciences Institute, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.