Optimized Ebselen-Based Inhibitors of Bacterial Ureases with Nontypical Mode of Action.
Macegoniuk, K., Tabor, W., Mazzei, L., Cianci, M., Giurg, M., Olech, K., Burda-Grabowska, M., Kaleta, R., Grabowiecka, A., Mucha, A., Ciurli, S., Berlicki, L.(2023) J Med Chem 66: 2054-2063
- PubMed: 36661843
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01799
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ZCY - PubMed Abstract:
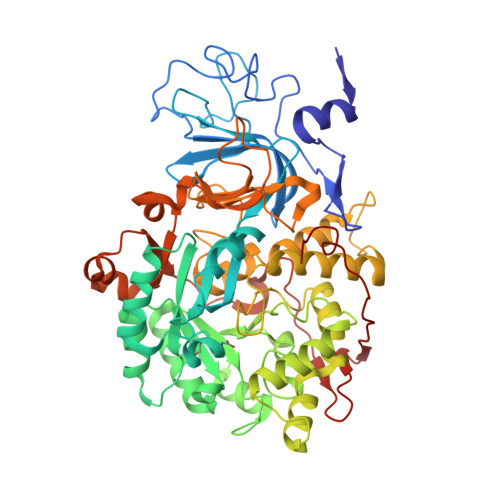
Screening of 25 analogs of Ebselen, diversified at the N-aromatic residue, led to the identification of the most potent inhibitors of Sporosarcina pasteurii urease reported to date. The presence of a dihalogenated phenyl ring caused exceptional activity of these 1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2 H )-ones, with K i value in a low picomolar range (<20 pM). The affinity was attributed to the increased ¦Ğ-¦Ğ and ¦Ğ-cation interactions of the dihalogenated phenyl ring with ¦ÁHis323 and ¦ÁArg339 during the initial step of binding. Complementary biological studies with selected compounds on the inhibition of ureolysis in whole Proteus mirabilis cells showed a very good potency (IC 50 < 25 nM in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer and IC 90 < 50 nM in a urine model) for monosubstituted N-phenyl derivatives. The crystal structure of S. pasteurii urease inhibited by one of the most active analogs revealed the recurrent selenation of the Cys322 thiolate, yielding an unprecedented Cys322-S-Se-Se chemical moiety.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioorganic Chemistry, Wroc?aw University of Science and Technology, Wybrze?e Wyspia¨½skiego 27, 50-370 Wroc?aw, Poland.