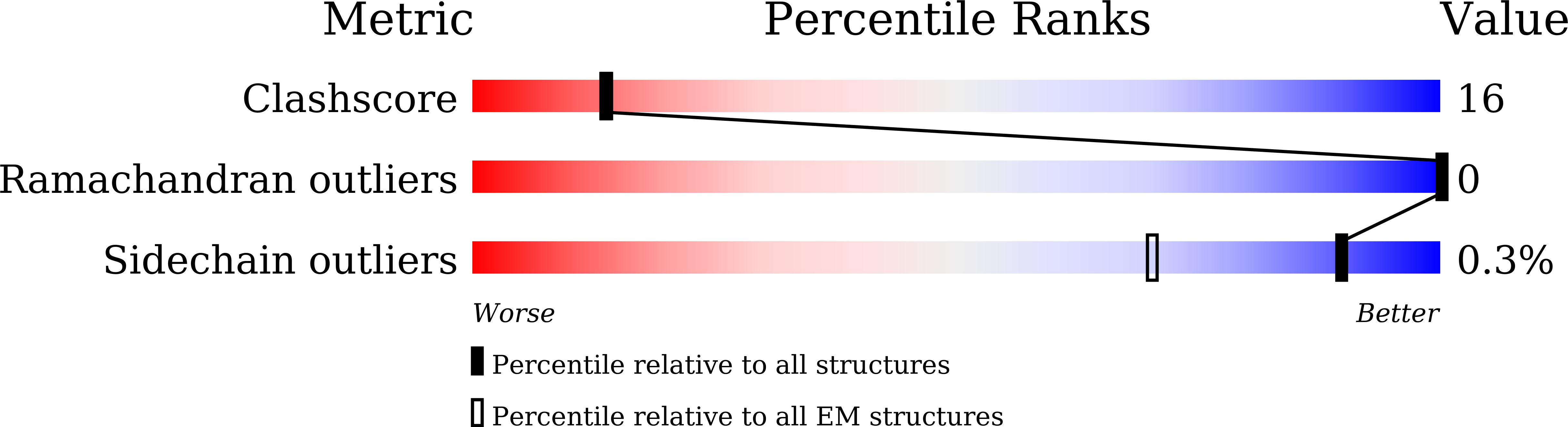Molecular insights into the activation mechanism of GPR156 in maintaining auditory function.
Ma, X., Chen, L.N., Liao, M., Zhang, L., Xi, K., Guo, J., Shen, C., Shen, D.D., Cai, P., Shen, Q., Qi, J., Zhang, H., Zang, S.K., Dong, Y.J., Miao, L., Qin, J., Ji, S.Y., Li, Y., Liu, J., Mao, C., Zhang, Y., Chai, R.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 10601-10601
- PubMed: 39638804
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-54681-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YJP, 8YK0 - PubMed Abstract:
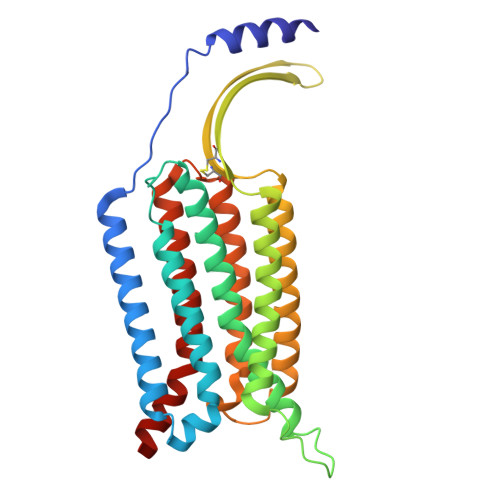
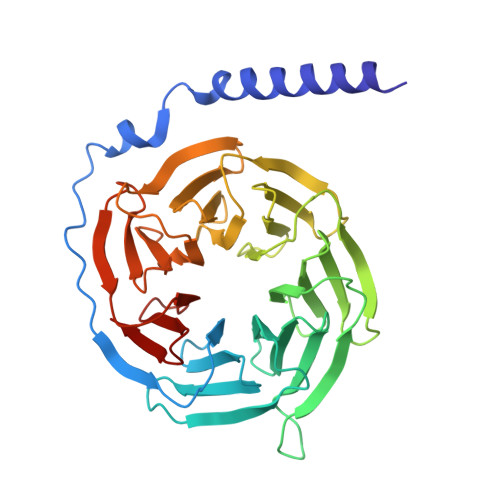
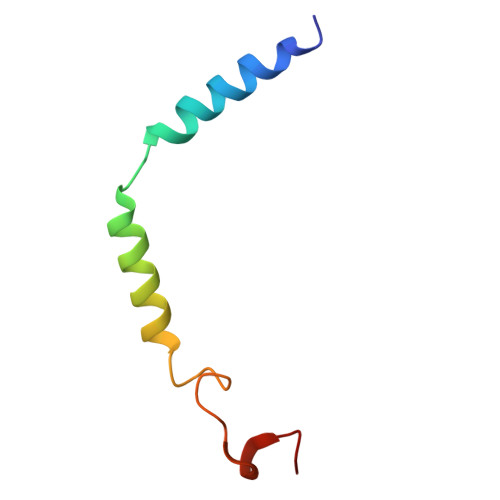
The class C orphan G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR156, which lacks the large extracellular region, plays a pivotal role in auditory function through G i2/3 . Here, we firstly demonstrate that GPR156 with high constitutive activity is essential for maintaining auditory function, and further reveal the structural basis of the sustained role of GPR156. We present the cryo-EM structures of human apo GPR156 and the GPR156-G i3 complex, unveiling a small extracellular region formed by extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) and the N-terminus. The GPR156 dimer in both apo state and G i3 protein-coupled state adopt a transmembrane (TM)5/6-TM5/6 interface, indicating the high constitutive activity of GPR156 in the apo state. Furthermore, C-terminus in G-bound subunit of GPR156 plays a dual role in promoting G protein binding within G-bound subunit while preventing the G-free subunit from binding to additional G protein. Together, these results explain how GPR156 constitutive activity is maintained through dimerization and provide a mechanistic insight into the sustained role of GPR156 in maintaining auditory function.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Digital Medical Engineering, Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Zhongda Hospital, School of Life Sciences and Technology, School of Medicine, Advanced Institute for Life and Health, Jiangsu Province High-Tech Key Laboratory for Bio-Medical Research, Southeast University, Nanjing, China.