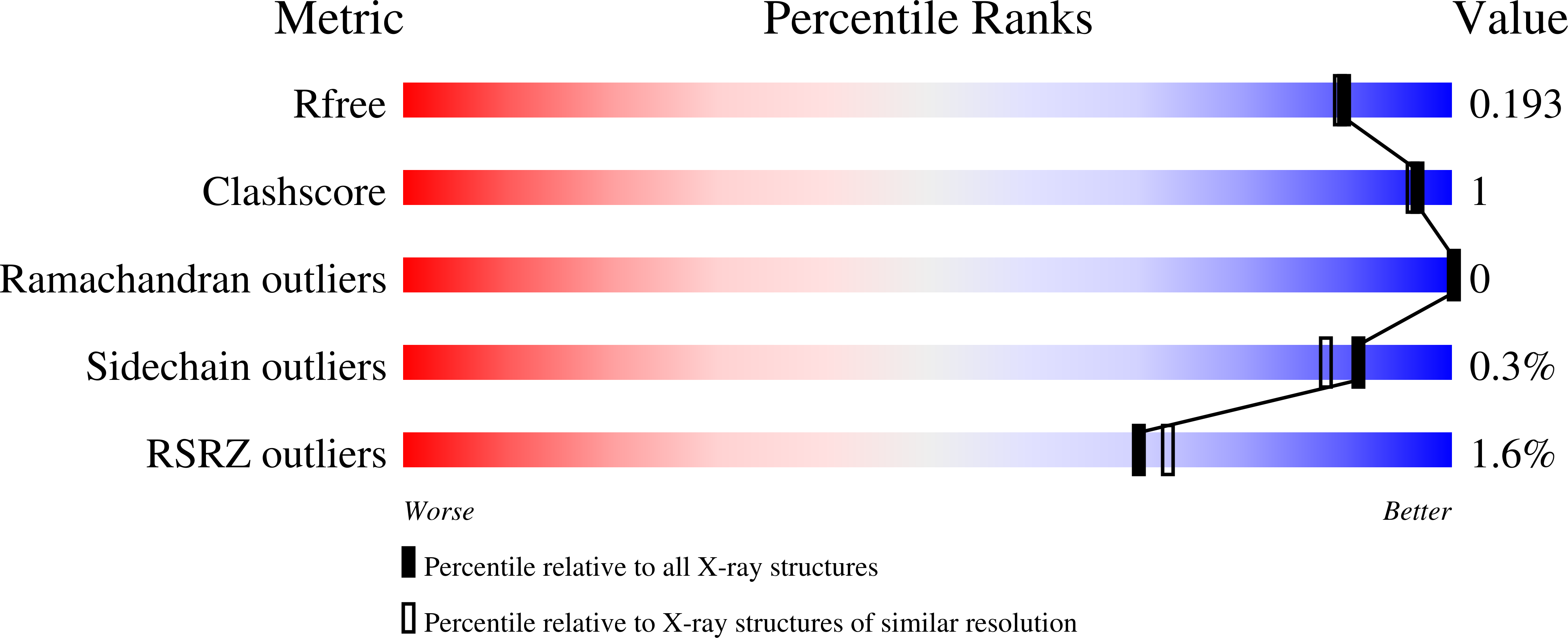
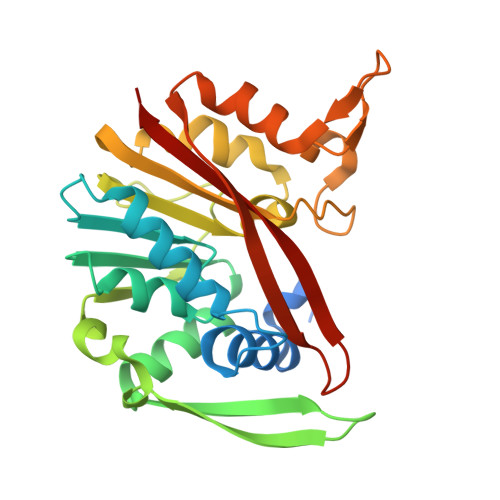
Structural and functional analysis of SAM-dependent N-methyltransferases involved in ovoselenol and ovothiol biosynthesis.
Ireland, K.A., Kayrouz, C.M., Abbott, M.L., Seyedsayamdost, M.R., Davis, K.M.(2025) Structure 33: 528-538.e5
- PubMed: 39862859
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2024.12.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BXH, 9BXJ, 9BXK, 9BXL, 9BXM, 9BXN - PubMed Abstract:
Thio/selenoimidazole N¦Đ-methyltransferases are an emerging family of enzymes catalyzing the final step in the production of the S/Se-containing histidine-derived antioxidants ovothiol and ovoselenol. These enzymes, prevalent in prokaryotes, show minimal sequence similarity to other methyltransferases, and the structural determinants of their reactivities remain poorly understood. Herein, we report ligand-bound crystal structures of OvsM from the ovoselenol pathway as well as a member of a previously unknown clade of standalone ovothiol-biosynthetic N¦Đ-methyltransferases, which we have designated OvoM. Unlike previously reported ovothiol methyltransferases, which are fused as a C-terminal domain to the sulfoxide synthase OvoA, OvoMs function independently. Comparative structural analyses reveal conserved, ligand-induced conformational changes, suggesting similar behavior in dual-domain OvoA enzymes. Mutagenesis supports a model where OvoA domain rearrangement facilitates substrate recognition via a critical Tyr residue in the domain linker. Biochemical studies identify an essential active-site Asp, likely serving as a catalytic base in the S N 2-like nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322, USA.