Quinazolinone-Based Anticancer Agents: Synthesis, Antiproliferative SAR, Antitubulin Activity, and Tubulin Co-crystal Structure.
Dohle, W., Jourdan, F.L., Menchon, G., Prota, A.E., Foster, P.A., Mannion, P., Hamel, E., Thomas, M.P., Kasprzyk, P.G., Ferrandis, E., Steinmetz, M.O., Leese, M.P., Potter, B.V.L.(2018) J Med Chem 61: 1031-1044
- PubMed: 29227648
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01474
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OSK - PubMed Abstract:
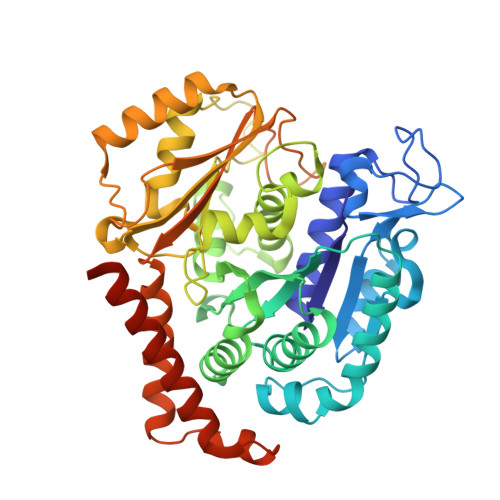
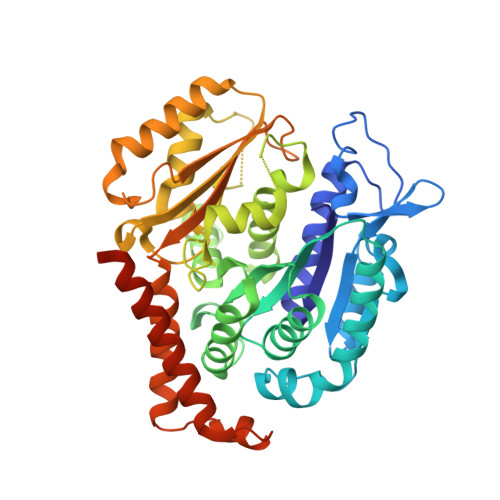
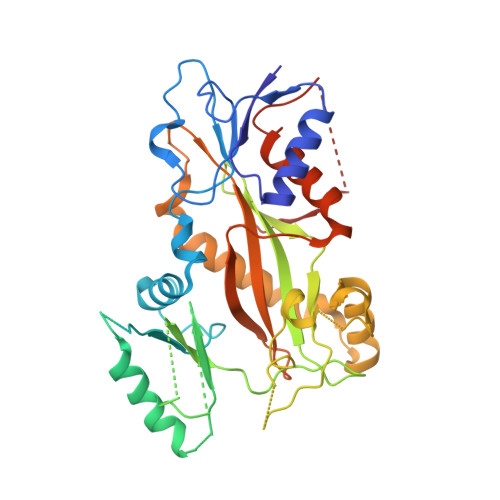
Quinazolinone-based anticancer agents were designed, decorated with functional groups from a 2-methoxyestradiol-based microtubule disruptor series, incorporating the aryl sulfamate motif of steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitors. The steroidal AB-ring system was mimicked, favoring conformations with an N-2 substituent occupying D-ring space. Evaluation against breast and prostate tumor cell lines identified 7b with DU-145 antiproliferative activity (GI 50 300 nM). A preliminary structure-activity relationship afforded compounds (e.g., 7j GI 50 50 nM) with activity exceeding that of the parent. Both 7b and 7j inhibit tubulin assembly in vitro and colchicine binding, and 7j was successfully co-crystallized with the ¦Á¦Â-tubulin heterodimer as the first of its class, its sulfamate group interacting positively at the colchicine binding site. Microtubule destabilization by 7j is likely achieved by preventing the curved-to-straight conformational transition in ¦Á¦Â-tubulin. Quinazolinone sulfamates surprisingly showed weak STS inhibition. Preliminary in vivo studies in a multiple myeloma xenograft model for 7b showed oral activity, confirming the promise of this template.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medicinal Chemistry & Drug Discovery, Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford , Mansfield Road, Oxford OX1 3QT, U.K.